How to Build a Powerful and Intelligent Question-Answering System by Using Tavily Search API, Chroma, Google Gemini LLMs, and the LangChain Framework
In this tutorial, we explain how to build a strong and smart system to leave questions by combining the strengths of Tavily Search API, Chroma, Google Gemini Llms and the Langchain framework. The pipeline takes advantage of the actual time search using Tavily, temporarily storing a semantic document with the Croma Vector store, and generating the contextual response through the Gemini model. These tools are combined with normative Langchain ingredients, such as runnablambda, ChatpromptTemplate, Thinkingbuffermory, and Googlegenerative It exceeds simple questions and answers by entering a mixed retrieval mechanism that verifies the stored implications before calling on new web search operations. The documents that are recovered intelligently, summarized and passed through the organized LLM router are coordinated, with interest in supporting the source, the user record, and the registration of confidence. Main functions such as advanced advanced engineering, analyzes and entities, and dynamic vector update, this pipeline is suitable for advanced use cases such as research aid, field summary, and smart agents.
!pip install -qU langchain-community tavily-python langchain-google-genai streamlit matplotlib pandas tiktoken chromadb langchain_core pydantic langchainWe install and upgrade a comprehensive set of libraries required to create an advanced AI search assistant. It includes Tavily-Python, Chromadb, LLM (Langchain-Google-Genai, Langchain), data processing (Pandas, Pydantic), Matplotlib, Spylit, and symbol (Tiktoken). These components are the basic basis for building a quality guarantee system in actual time.
import os
import getpass
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import json
import time
from typing import List, Dict, Any, Optional
from datetime import datetimeWe import the basic Python libraries used in the notebook. It includes standard libraries for environmental variables, safe inputs, time tracking, and data types (OS, GetPass, Time, Writing, Datime). In addition, it brings basic data science tools such as Pandas, Matplotlib and Numby to process data, perception and numerical calculations, as well as JSON to analyze structured data.
if "TAVILY_API_KEY" not in os.environ:
os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("Enter Tavily API key: ")
if "GOOGLE_API_KEY" not in os.environ:
os.environ["GOOGLE_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("Enter Google API key: ")
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format="%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s")
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)We create API keys safely for Tavily and Google Gemini by pushing users only if they are not already assigned to the environment, ensuring safe and repeated access to external services. It also creates a unified registration setting using the Python registration unit, which helps to monitor the implementation of implementation and pick up errors or error through the notebook.
from langchain_community.retrievers import TavilySearchAPIRetriever
from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain_core.documents import Document
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser, JsonOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, SystemMessagePromptTemplate, HumanMessagePromptTemplate
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough, RunnableLambda
from langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAI, GoogleGenerativeAIEmbeddings
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.chains.summarize import load_summarize_chain
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemoryWe import the main components of the Langchain ecosystem. It brings TavilySearchraPiretriever to real time search on the web, Chroma to store vectors, Googlegenerativeii units for chat and inclusion models. Langchain units such as Chatprompttemplate, Runnablambda, ThipctionBuffermeMory and Output Persers are amazing flexible construction, memory processing and pipelines’ implementation.
class SearchQueryError(Exception):
"""Exception raised for errors in the search query."""
pass
def format_docs(docs):
formatted_content = []
for i, doc in enumerate(docs):
metadata = doc.metadata
source = metadata.get('source', 'Unknown source')
title = metadata.get('title', 'Untitled')
score = metadata.get('score', 0)
formatted_content.append(
f"Document {i+1} [Score: {score:.2f}]:n"
f"Title: {title}n"
f"Source: {source}n"
f"Content: {doc.page_content}n"
)
return "nn".join(formatted_content)We define two basic elements for research and deal with documents. The Searchqueryroror category creates an exception to manage unconventional or failed search inquiries. Format_docs function processes the list of documents that were recovered by extracting descriptive data such as the address and source and the degree of importance and coordinating it in a readable and readable series.
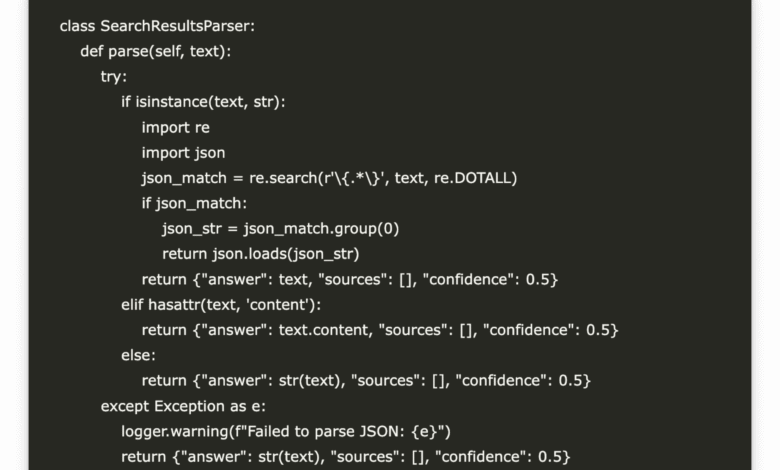
class SearchResultsParser:
def parse(self, text):
try:
if isinstance(text, str):
import re
import json
json_match = re.search(r'{.*}', text, re.DOTALL)
if json_match:
json_str = json_match.group(0)
return json.loads(json_str)
return {"answer": text, "sources": [], "confidence": 0.5}
elif hasattr(text, 'content'):
return {"answer": text.content, "sources": [], "confidence": 0.5}
else:
return {"answer": str(text), "sources": [], "confidence": 0.5}
except Exception as e:
logger.warning(f"Failed to parse JSON: {e}")
return {"answer": str(text), "sources": [], "confidence": 0.5}Searchsultsparser category provides a strong way to extract organized information from LLM responses. It tries to analyze a JSON chain from the form of the form, and return to coordinating a normal text response if the analysis fails. It treats the outputs of the chain safely and messages, ensuring consistent treatment in the direction of the estuary. In the event of errors, it records a warning and reserved backfire that contains the initial answer, empty sources, and the degree of virtual confidence, which enhances the endurance of the system’s mistake.
class EnhancedTavilyRetriever:
def __init__(self, api_key=None, max_results=5, search_depth="advanced", include_domains=None, exclude_domains=None):
self.api_key = api_key
self.max_results = max_results
self.search_depth = search_depth
self.include_domains = include_domains or []
self.exclude_domains = exclude_domains or []
self.retriever = self._create_retriever()
self.previous_searches = []
def _create_retriever(self):
try:
return TavilySearchAPIRetriever(
api_key=self.api_key,
k=self.max_results,
search_depth=self.search_depth,
include_domains=self.include_domains,
exclude_domains=self.exclude_domains
)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to create Tavily retriever: {e}")
raise
def invoke(self, query, **kwargs):
if not query or not query.strip():
raise SearchQueryError("Empty search query")
try:
start_time = time.time()
results = self.retriever.invoke(query, **kwargs)
end_time = time.time()
search_record = {
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat(),
"query": query,
"num_results": len(results),
"response_time": end_time - start_time
}
self.previous_searches.append(search_record)
return results
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Search failed: {e}")
raise SearchQueryError(f"Failed to perform search: {str(e)}")
def get_search_history(self):
return self.previous_searchesEndustantttavilyriever category is a dedicated cover around Tavilysearchraptriever, which adds more flexibility, control and tracking in searches. It supports advanced features such as reducing the depth of research, inserting the field/exclusion filters, and formed results. The Invoke method performs searches on the web and tracks the definition data of each query (time character, response time, number of results), and storing subsequent analysis.
class SearchCache:
def __init__(self):
self.embedding_function = GoogleGenerativeAIEmbeddings(model="models/embedding-001")
self.vector_store = None
self.text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=200)
def add_documents(self, documents):
if not documents:
return
try:
if self.vector_store is None:
self.vector_store = Chroma.from_documents(
documents=documents,
embedding=self.embedding_function
)
else:
self.vector_store.add_documents(documents)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to add documents to cache: {e}")
def search(self, query, k=3):
if self.vector_store is None:
return []
try:
return self.vector_store.similarity_search(query, k=k)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Vector search failed: {e}")
return []The Searchcache category implements a temporary semantic storage layer that stores and recovered documents using vectors to search for effective similarities. Googlegenerativeaiembedds is used to convert documents into dense tankers and store them in the Chroma vector database. The ADD_Documents method creates or updates the vector store, while the method of searching for the rapid recovery of the most relevant stored documents allows the most relevant semantic similarity. This reduces the recurrent application programming interface calls and improves response times for repeated or relevant information, as a lightweight hybrid memory layer in AI’s auxiliary pipeline.
search_cache = SearchCache()
enhanced_retriever = EnhancedTavilyRetriever(max_results=5)
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history", return_messages=True)
system_template = """You are a research assistant that provides accurate answers based on the search results provided.
Follow these guidelines:
1. Only use the context provided to answer the question
2. If the context doesn't contain the answer, say "I don't have sufficient information to answer this question."
3. Cite your sources by referencing the document numbers
4. Don't make up information
5. Keep the answer concise but complete
Context: {context}
Chat History: {chat_history}
"""
system_message = SystemMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(system_template)
human_template = "Question: {question}"
human_message = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(human_template)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([system_message, human_message])
We create the basic components of the semantic searchcheche, and the Tovilyriever for the web -based inquiries, and the Buffermemory conversation to keep the chat record via the turns. It also determines an organized claim using Chatprompttemplate, and directing LLM to work as a search assistant. The claim imposes strict rules for real accuracy, the use of context, the martyrdom of a source, the short response, and the guarantee of reliable and institutional responses.
def get_llm(model_name="gemini-2.0-flash-lite", temperature=0.2, response_mode="json"):
try:
return ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(
model=model_name,
temperature=temperature,
convert_system_message_to_human=True,
top_p=0.95,
top_k=40,
max_output_tokens=2048
)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to initialize LLM: {e}")
raise
output_parser = SearchResultsParser()
We define the fun_lm function, which is to create the Google Gemini language model with training parameters such as the name of the model, the temperature, and the decoding settings (for example, Top_P, Top_K, and Max codes). It guarantees durability by addressing errors to create a failed model. An example of Searchchresultsparser is also created to unify the initial responses of LLM, allowing consistent answers and descriptive data.
def plot_search_metrics(search_history):
if not search_history:
print("No search history available")
return
df = pd.DataFrame(search_history)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(range(len(df)), df['response_time'], marker="o")
plt.title('Search Response Times')
plt.xlabel('Search Index')
plt.ylabel('Time (seconds)')
plt.grid(True)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.bar(range(len(df)), df['num_results'])
plt.title('Number of Results per Search')
plt.xlabel('Search Index')
plt.ylabel('Number of Results')
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
The Plot_Search_meetrics function imagines performance trends from previous queries using Matplotlib. It turns the search record into a data system and establishes two sub -graduates: one shows the time of response to each research and the other shows the number of results that have been returned. This helps in analyzing the efficiency of the system and the quality of the research over time, which helps developers to control the recovery or determine the bottlenecks in the real world.
def retrieve_with_fallback(query):
cached_results = search_cache.search(query)
if cached_results:
logger.info(f"Retrieved {len(cached_results)} documents from cache")
return cached_results
logger.info("No cache hit, performing web search")
search_results = enhanced_retriever.invoke(query)
search_cache.add_documents(search_results)
return search_results
def summarize_documents(documents, query):
llm = get_llm(temperature=0)
summarize_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"""Create a concise summary of the following documents related to this query: {query}
{documents}
Provide a comprehensive summary that addresses the key points relevant to the query.
"""
)
chain = (
{"documents": lambda docs: format_docs(docs), "query": lambda _: query}
| summarize_prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
return chain.invoke(documents)These two functions enhance the intelligence and efficiency of the assistant. The RetrieVE_With_fallback function does a mixed retrieval mechanism: first trying to bring the relevant documents in a semantic manner of the local Chroma cache, and if it does not succeed, it is due to research on the Internet in an actual time, which hides the new results of future use. Meanwhile, Supplaize_documents provides Gemini LLM with brief summaries of the recovered documents, which are guided by a organization that guarantees the link to inquiries. Together, it provides low -construction, informational, and context responses.
def advanced_chain(query_engine="enhanced", model="gemini-1.5-pro", include_history=True):
llm = get_llm(model_name=model)
if query_engine == "enhanced":
retriever = lambda query: retrieve_with_fallback(query)
else:
retriever = enhanced_retriever.invoke
def chain_with_history(input_dict):
query = input_dict["question"]
chat_history = memory.load_memory_variables({})["chat_history"] if include_history else []
docs = retriever(query)
context = format_docs(docs)
result = prompt.invoke({
"context": context,
"question": query,
"chat_history": chat_history
})
memory.save_context({"input": query}, {"output": result.content})
return llm.invoke(result)
return RunnableLambda(chain_with_history) | StrOutputParser()The Advanced_chain function determines a logical workflow to one to the end of the user’s information using the actual or actual search search. It creates the specified gemini model, selects the retrieval strategy (temporarily stored reserves or direct search), creates a response pipeline that includes the chat record (if enabled), coordinates documents in the context, and demands LLM to use a system guided system. The series also records the interaction in memory and returns the final answer, and is analyzed in a clean text. This design allows flexible experience with models and retrieval strategies while maintaining conversation cohesion.
qa_chain = advanced_chain()
def analyze_query(query):
llm = get_llm(temperature=0)
analysis_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"""Analyze the following query and provide:
1. Main topic
2. Sentiment (positive, negative, neutral)
3. Key entities mentioned
4. Query type (factual, opinion, how-to, etc.)
Query: {query}
Return the analysis in JSON format with the following structure:
{{
"topic": "main topic",
"sentiment": "sentiment",
"entities": ["entity1", "entity2"],
"type": "query type"
}}
"""
)
chain = analysis_prompt | llm | output_parser
return chain.invoke({"query": query})
print("Advanced Tavily-Gemini Implementation")
print("="*50)
query = "what year was breath of the wild released and what was its reception?"
print(f"Query: {query}")Prepare the final components of the smart assistant. QA_Chain is the collected thinking pipeline ready to process the user’s information using Gemini and Memory Response and Gemini. Analyze_query function performs a lightweight semantic analysis on the query, extracting the main theme, feeling, entities, and querying type using the Gemini model and asking JSON organization. The query, for example, explains about the breathing and reception of Wild’s release, how the assistant is running and prepared for complete inference and semantic interpretation. The printed title is the beginning of interactive implementation.
try:
print("nSearching for answer...")
answer = qa_chain.invoke({"question": query})
print("nAnswer:")
print(answer)
print("nAnalyzing query...")
try:
query_analysis = analyze_query(query)
print("nQuery Analysis:")
print(json.dumps(query_analysis, indent=2))
except Exception as e:
print(f"Query analysis error (non-critical): {e}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error in search: {e}")
history = enhanced_retriever.get_search_history()
print("nSearch History:")
for i, h in enumerate(history):
print(f"{i+1}. Query: {h['query']} - Results: {h['num_results']} - Time: {h['response_time']:.2f}s")
print("nAdvanced search with domain filtering:")
specialized_retriever = EnhancedTavilyRetriever(
max_results=3,
search_depth="advanced",
include_domains=["nintendo.com", "zelda.com"],
exclude_domains=["reddit.com", "twitter.com"]
)
try:
specialized_results = specialized_retriever.invoke("breath of the wild sales")
print(f"Found {len(specialized_results)} specialized results")
summary = summarize_documents(specialized_results, "breath of the wild sales")
print("nSummary of specialized results:")
print(summary)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error in specialized search: {e}")
print("nSearch Metrics:")
plot_search_metrics(history)
We show the full pipeline at work. It performs a search using QA_chain, shows the created answer, then analyzes inquiries about feelings, subject, entities and type. It also recalls and prints the date of searching for each inquiry, response time, and number of results. It also runs a candidate for the field focusing on Nintendo sites, summarizing the results, and depicting the search performance using Plot_search_meetrics, providing a comprehensive vision of the assistant capabilities in the use of actual time.
In conclusion, this educational program for users allows a comprehensive plan to create a confrontable and developed rag system that embodies web intelligence in the actual time with AI to conversation. Search Search Tavily applications for users allows fresh and self -relevant content to pull directly from the web. GIMINI LLM adds strong possibilities for thinking and summarizing, while the Langchain abstract layer allows a smooth format between memory, implications and typical outputs. Implementation includes advanced features such as domain liquidation, query analysis (feelings, subject, entity extraction), and backup strategies using semantic cache designed with Chroma and Googlegenerative Also, organized recording panels, error treatment, transparency analyzes and diagnoses are provided to spread the real world.
Check the Kulayb book. All the credit for this research goes to researchers in this project. Also, do not hesitate to follow us twitter And do not forget to join 90k+ ml subreddit.
Asif Razzaq is the CEO of Marktechpost Media Inc .. As a pioneer and vision engineer, ASIF is committed to harnessing the potential of artificial intelligence for social goodness. His last endeavor is to launch the artificial intelligence platform, Marktechpost, which highlights its in -depth coverage of machine learning and deep learning news, which is technically sound and can be easily understood by a wide audience. The platform is proud of more than 2 million monthly views, which shows its popularity among the masses.
🚨 Genai building you can trust. ⭐ Parlant is your open source of control, compatible, and calm-calm on GitHub! (It was promoted)
Don’t miss more hot News like this! Click here to discover the latest in AI news!
2025-05-18 03:19:00