What neuroscience can tell AI about learning in continuously changing environments
Wong, B. B. M. & Candolin, U. Behavioral responses to changing environments. Behav. Ecol. 26, 665–673 (2014).
Google Scholar
Mazza, V. & Šlipogor, V. Behavioral flexibility and novel environments: integrating current perspectives for future directions. Curr. Zool. 70, 304–309 (2024).
Google Scholar
Jones, C. B. Behavioral Flexibility in Primates: Causes and Consequences (Springer, 2005).
Finn, C., Abbeel, P. & Levine, S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks. In Proc. 34th International Conference on Machine Learning Vol. 70, 1126–1135 (PMLR, 2017).
Koutra, D. et al. Towards agentic AI for science: hypothesis generation, comprehension, quantification, and validation. In ICLR 2025 Workshop Proposals (2025).
Faraboschi, P., Giles, E., Hotard, J., Owczarek, K. & Wheeler, A. Reducing the barriers to entry for foundation model training. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2404.08811 (2024).
Magee, J. C. & Grienberger, C. Synaptic plasticity forms and functions. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 43, 95–117 (2020).
Google Scholar
Wu, Y. & Maass, W. A simple model for behavioral time scale synaptic plasticity (BTSP) provides content addressable memory with binary synapses and one-shot learning. Nat. Commun. 16, 342 (2025).
Google Scholar
Zhao, C. et al. Is chain-of-thought reasoning of LLMs a mirage? A data distribution lens. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2508.01191 (2025).
Parisi, G. I., Kemker, R., Part, J. L., Kanan, C. & Wermter, S. Continual lifelong learning with neural networks: a review. Neural Netw. 113, 54–71 (2019).
Google Scholar
Kudithipudi, D. et al. Biological underpinnings for lifelong learning machines. Nat. Mach. Intell. 4, 196–210 (2022).
Google Scholar
Gupta, R. et al. Personalized artificial general intelligence (AGI) via neuroscience-inspired continuous learning systems. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2504.20109 (2025).
Mazurek, S., Caputa, J., Argasiński, J. K. & Wielgosz, M. Three-factor learning in spiking neural networks: an overview of methods and trends from a machine learning perspective. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2504.05341 (2025).
Bittner, K. C., Milstein, A. D., Grienberger, C., Romani, S. & Magee, J. C. Behavioral time scale synaptic plasticity underlies CA1 place fields. Science 357, 1033–1036 (2017).
Google Scholar
Grazzi, R., Siems, J. N., Schrodi, S., Brox, T. & Hutter, F. Is mamba capable of in-context learning? In Proc. International Conference on Automated Machine Learning 1–26 (AutoML, 2024).
Singh, A. K. et al. The transient nature of emergent in-context learning in transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 36, 27801–27819 (2023).
Bai, Y., Chen, F., Wang, H., Xiong, C. & Mei, S. Transformers as statisticians: provable in-context learning with in-context algorithm selection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 36, 57125–57211 (2023).
Brown, T. B. et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 1877–1901 (2020).
Dai, D. et al. Why can GPT learn incontext? Language models implicitly perform gradient descent as meta-optimizers. In Workshop on Mathematical and Empirical Understanding of Foundation Models (2023).
Garg, S., Tsipras, D., Liang, P. S. & Valiant, G. What can transformers learn in-context? A case study of simple function classes. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 30583–30598 (2022).
Wei, J. et al. Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 24824–24837 (2022).
Liu, L. et al. On the variance of the adaptive learning rate and beyond. In Proc. 8th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2020).
Hemmer, C. J. & Durstewitz, D. True zero-shot inference of dynamical systems preserving long-term statistics. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 39, 1–44 (2025).
Touvron, H. et al. Llama 2: open foundation and fine-tuned chat models. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2307.09288 (2023).
Goodfellow, I. J., Mirza, M., Xiao, D., Courville, A. & Bengio, Y. An empirical investigation of catastrophic forgetting in gradient-based neural networks. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6211 (2013).
Kirkpatrick, J. et al. Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in neural networks. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, 3521–3526 (2017).
Google Scholar
Ramasesh, V., Lewkowycz, A. & Dyer, E. Effect of scale on catastrophic forgetting in neural networks. In Proc. 10th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2022).
Carpenter, G. A. & Grossberg, S. ART 2: self-organization of stable category recognition codes for analog input patterns. Appl. Opt. 26, 4919–4930 (1987).
Google Scholar
Jung, D. et al. New insights for the stability-plasticity dilemma in online continual learning. In Proc. 11th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2023).
McCloskey, M. & Cohen, N. J. Catastrophic interference in connectionist networks: the sequential learning problem. Psychol. Learn. Motiv. 24, 109–165 (1989).
Google Scholar
French, R. M. Catastrophic forgetting in connectionist networks. Trends Cogn. Sci. 3, 128–135 (1999).
Google Scholar
Wang, Z., Li, Y., Shen, L. & Huang, H. A unified and general framework for continual learning. In Proc. 12th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2024).
Wang, L., Zhang, X., Su, H. & Zhu, J. A comprehensive survey of continual learning: theory, method and application. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell 46, 5362–5383 (2024).
Zheng, W.-L., Wu, Z., Hummos, A., Yang, G. R. & Halassa, M. M. Rapid context inference in a thalamocortical model using recurrent neural networks. Nat. Commun. 15, 8275 (2024).
Google Scholar
Nguyen, C. V., Li, Y., Bui, T. D. & Turner, R. E. Variational continual learning. In Proc. 6th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2018).
Wu, Y., Huang, L.-K., Wang, R., Meng, D. & Wei, Y. Meta continual learning revisited: implicitly enhancing online Hessian approximation via variance reduction. In Proc. 12th International Conference on Learning Representations Vol. 2 (ICLR, 2024).
Li, Z. & Hoiem, D. Learning without forgetting. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40, 2935–2947 (2018).
Google Scholar
McDonnell, M. D., Gong, D., Parvaneh, A., Abbasnejad, E. & Van den Hengel, A. Ranpac: random projections and pre-trained models for continual learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 36, 12022–12053 (2023).
Ostapenko, O., Rodriguez, P., Caccia, M. & Charlin, L. Continual learning via local module composition. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 30298–30312 (2021).
Sorscher, B., Ganguli, S. & Sompolinsky, H. Neural representational geometry underlies few-shot concept learning. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 119, e2200800119 (2022).
Google Scholar
Riemer, M. et al. Learning to learn without forgetting by maximizing transfer and minimizing interference. In Proc. 7th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2019).
Shin, H., Lee, J. K., Kim, J. & Kim, J. Continual learning with deep generative replay. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30, 2994–3003 (2017).
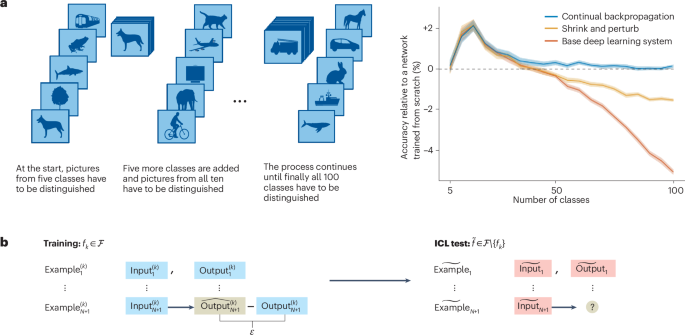
Dohare, S. et al. Loss of plasticity in deep continual learning. Nature 632, 768–774 (2024).
Google Scholar
van de Ven, G. M., Tuytelaars, T. & Tolias, A. S. Three types of incremental learning. Nat. Mach. Intell. 4, 1185–1197 (2022).
Google Scholar
Houlsby, N. Parameter-efficient transfer learning for NLP. In Proc. 36th International Conference on Machine Learning Vol. 97, 2790–2799 (PMLR, 2019).
Hu, E. J. et al. LoRA: low-rank adaptation of large language models. In Proc. 10th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2022).
Mendez, J. A., van Seijen, H. & EATON, E. Modular lifelong reinforcement learning via neural composition. In Proc.10th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2022).
Graves, A., Wayne, G. & Danihelka, I. Neural Turing machines. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1410.5401 (2014).
Lewis, P. et al. Retrieval-augmented generation for knowledge-intensive NLP tasks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 9459–9474 (2020).
Yu, Y. et al. RankRAG: unifying context ranking with retrieval-augmented generation in LLMs. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 37, 121156–121184 (2024).
Santoro, A., Bartunov, S., Botvinick, M., Wierstra, D. & Lillicrap, T. Meta-learning with memory-augmented neural networks. In Proc. 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning Vol. 48, 1842–(PMLR, 2016).
Skaggs, W. E. & McNaughton, B. L. Replay of neuronal firing sequences in rat hippocampus during sleep following spatial experience. Science 271, 1870–1873 (1996).
Google Scholar
Mallory, C. S., Widloski, J. & Foster, D. J. The time course and organization of hippocampal replay. Science 387, 541–548 (2025).
Google Scholar
Grienberger, C. & Magee, J. C. Entorhinal cortex directs learning-related changes in CA1 representations. Nature 611, 554–562 (2022).
Google Scholar
Krueger, D. et al. Out-of-distribution generalization via risk extrapolation (REx). In Proc. 38th International Conference on Machine Learning Vol. 139, 5815–5826 (PMLR, 2021).
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R. & Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction (Springer, 2009).
Göring, N. A., Hess, F., Brenner, M., Monfared, Z. & Durstewitz, D. Out-of-domain generalization in dynamical systems reconstruction. In Proc. 41st International Conference on Machine Learning Vol. 235, 16071–16114 (PMLR, 2024).
Lampinen, A. K., Chan, S. C., Singh, A. K. & Shanahan, M. The broader spectrum of in-context learning. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.03782 (2024).
Li, Y., Ildiz, M. E., Papailiopoulos, D. & Oymak, S. Transformers as algorithms: generalization and stability in in-context learning. In Proc. 40th International Conference on Machine Learning Vol. 202, 19565–19594 (PMLR, 2023).
Li, Y., Wei, X., Zhao, H. & Ma, T. Can Mamba in-context learn task mixtures? In ICML 2024 Workshop on In-Context Learning (2024).
Oswald, J. V. et al. Transformers learn in-context by gradient descent. In Proc. 40th International Conference on Machine Learning Vol. 202, 35151–35174 (PMLR, 2023).
Shen, L., Mishra, A. & Khashabi, D. Position: do pretrained transformers learn in-context by gradient descent? In Proc. 41st International Conference on Machine Learning Vol. 235, 44712–44740 (PMLR, 2024).
Li, J., Hou, Y., Sachan, M. & Cotterell, R. What do language models learn in context? The structured task hypothesis. In Proc. 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics Vol. 1, 12365–12379 (Association for Computational Linguistics, 2024).
Deutch, G., Magar, N., Natan, T. & Dar, G. In-context learning and gradient descent revisited. In Proc. 2024 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (Volume 1: Long Papers) 1017–1028 (Association for Computational Linguistics, 2024).
Yadlowsky, S., Doshi, L. & Tripuraneni, N. Pretraining data mixtures enable narrow model selection capabilities in transformer models. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.00871 (2023).
Hahn, M. & Goyal, N. A theory of emergent in-context learning as implicit structure induction. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.07971 (2023).
Chan, S. et al. Data distributional properties drive emergent in-context learning in transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 18878–18891 (2022).
Snell, C., Lee, J., Xu, K. & Kumar, A. Scaling LLM test-time compute optimally can be more effective than scaling model parameters. In Proc. 13th International Conference on Learning Representations, 1-37 (ICLR, 2025).
Domjan, M. The Principles of Learning and Behavior 7th edn (Cengage Learning, 2014).
Shettleworth, S. J. Cognition, Evolution, and Behavior 2nd edn (Oxford Univ. Press, 2009).
Bähner, F. et al. Abstract rule learning promotes cognitive flexibility in complex environments across species. Nat. Commun. 16, 5396 (2025).
Google Scholar
Bouchacourt, F., Tafazoli, S., Mattar, M. G., Buschman, T. J. & Daw, N. D. Fast rule switching and slow rule updating in a perceptual categorization task. eLife 11, e82531 (2022).
Google Scholar
Stokes, M. G. et al. Dynamic coding for cognitive control in prefrontal cortex. Neuron 78, 364–375 (2013).
Google Scholar
Beiran, M., Meirhaeghe, N., Sohn, H., Jazayeri, M. & Ostojic, S. Parametric control of flexible timing through low-dimensional neural manifolds. Neuron 111, 739–753.e738 (2023).
Google Scholar
Evenden, J. L. & Robbins, T. W. Win–stay behaviour in the rat. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. B 36, 1–26 (1984).
Google Scholar
Cohen, Y., Schneidman, E. & Paz, R. The geometry of neuronal representations during rule learning reveals complementary roles of cingulate cortex and putamen. Neuron 109, 839–851.e839 (2021).
Google Scholar
Tang, H., Costa, V. D., Bartolo, R. & Averbeck, B. B. Differential coding of goals and actions in ventral and dorsal corticostriatal circuits during goal-directed behavior. Cell Rep. 38, 110198 (2022).
Google Scholar
Passecker, J. et al. Activity of prefrontal neurons predict future choices during gambling. Neuron 101, 152–164.e157 (2019).
Google Scholar
Pereira-Obilinovic, U., Hou, H., Svoboda, K. & Wang, X.-J. Brain mechanism of foraging: reward-dependent synaptic plasticity versus neural integration of values. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 121, e2318521121 (2024).
Google Scholar
Egner, T. & Siqi-Liu, A. Insights into control over cognitive flexibility from studies of task-switching. Curr. Opin. Syst. Biol. 55, 101342 (2024).
Uddin, L. Q. Cognitive and behavioural flexibility: neural mechanisms and clinical considerations. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 22, 167–179 (2021).
Google Scholar
Durstewitz, D. & Seamans, J. K. The dual-state theory of prefrontal cortex dopamine function with relevance to catechol-O-methyltransferase genotypes and schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 64, 739–749 (2008).
Google Scholar
Goudar, V., Peysakhovich, B., Freedman, D. J., Buffalo, E. A. & Wang, X.-J. Schema formation in a neural population subspace underlies learning-to-learn in flexible sensorimotor problem-solving. Nat. Neurosci. 26, 879–890 (2023).
Google Scholar
Driscoll, L. N., Shenoy, K. & Sussillo, D. Flexible multitask computation in recurrent networks utilizes shared dynamical motifs. Nat. Neurosci. 27, 1349–1363 (2024).
Google Scholar
Bakermans, J. J. W., Warren, J., Whittington, J. C. R. & Behrens, T. E. J. Constructing future behavior in the hippocampal formation through composition and replay. Nat. Neurosci. 28, 1061–1072 (2025).
Google Scholar
Gallistel, C. R., Fairhurst, S. & Balsam, P. The learning curve: Implications of a quantitative analysis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 13124–13131 (2004).
Google Scholar
Papachristos, E. B. & Gallistel, C. Autoshaped head poking in the mouse: a quantitative analysis of the learning curve. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 85, 293–308 (2006).
Google Scholar
Durstewitz, D., Vittoz, N. M., Floresco, S. B. & Seamans, J. K. Abrupt transitions between prefrontal neural ensemble states accompany behavioral transitions during rule learning. Neuron 66, 438–448 (2010).
Google Scholar
Powell, N. J. & Redish, A. D. Representational changes of latent strategies in rat medial prefrontal cortex precede changes in behaviour. Nat. Commun. 7, 12830 (2016).
Google Scholar
Karlsson, M. P., Tervo, D. G. R. & Karpova, A. Y. Network resets in medial prefrontal cortex mark the onset of behavioral uncertainty. Science 338, 135–139 (2012).
Google Scholar
Russo, E. et al. Coordinated prefrontal state transition leads extinction of reward-seeking behaviors. J. Neurosci. 41, 2406–2419 (2021).
Google Scholar
Miles, J. T., Mullins, G. L. & Mizumori, S. J. Flexible decision-making is related to strategy learning, vicarious trial and error, and medial prefrontal rhythms during spatial set-shifting. Learn. Mem. 31, a053911 (2024).
Google Scholar
Gottlieb, J. & Oudeyer, P.-Y. Towards a neuroscience of active sampling and curiosity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 19, 758–770 (2018).
Google Scholar
Friston, K. The free-energy principle: a unified brain theory? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 11, 127–138 (2010).
Google Scholar
Burda, Y., Edwards, H., Storkey, A. & Klimov, O. Exploration by random network distillation. In Proc. 7th International Conference on Learning Representations 1–17 (ICLR, 2019).
Li, D. et al. A survey on deep active learning: recent advances and new frontiers. IEEE Trans. Neural. Networks. Learn. Syst. 36, 5879–5899 (2025).
Google Scholar
Millidge, B. Deep active inference as variational policy gradients. J. Math. Psychol. 96, 102348 (2020).
Google Scholar
Pathak, D., Agrawal, P., Efros, A. A. & Darrell, T. Curiosity-driven exploration by self-supervised prediction. In Proc. 34th International Conference on Machine Learning Vol. 70, 2778–2787 (PMLR, 2017).
Settles, B. Active Learning Literature Survey 1648 (Univ. Wisconsin-Madison Department of Computer Sciences, 1995).
van der Himst, O. & Lanillos, P. in Active Inference (eds Verbelen, T. et al.) 61–71 (Springer, 2020).
Branicky, M. S. Universal computation and other capabilities of hybrid and continuous dynamical systems. Theor. Comput. Sci. 138, 67–100 (1995).
Google Scholar
Koiran, P., Cosnard, M. & Garzon, M. Computability with low-dimensional dynamical systems. Theor. Comput. Sci. 132, 113–128 (1994).
Google Scholar
Siegelmann, H. T. & Sontag, E. D. On the computational power of neural nets. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 50, 132–150 (1995).
Google Scholar
Fernando, J. & Guitchounts, G. Transformer dynamics: a neuroscientific approach to interpretability of large language models. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.12131 (2025).
Geshkovski, B., Letrouit, C., Polyanskiy, Y., & Rigollet, P. A mathematical perspective on transformers. Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 62, 427-479 (2025).
Mikhaeil, J. M., Monfared, Z. & Durstewitz, D. On the difficulty of learning chaotic dynamics with RNNs. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. Vol. 35, 11297–11312 (2022).
Monfared, Z. & Durstewitz, D. Transformation of ReLU-based recurrent neural networks from discrete-time to continuous-time. In Proc. 37th International Conference on Machine Learning Vol. 119, 6999–7009 (PMLR, 2020).
Eisenmann, L., Monfared, Z., Göring, N. & Durstewitz, D. Bifurcations and loss jumps in RNN training. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 36, 70511–70547 (2023).
Ibayashi, H. & Imaizumi, M. Why does sgd prefer flat minima?: Through the lens of dynamical systems. In AAAI Workshop When Machine Learning meets Dynamical Systems: Theory and Applications (2023).
Şimşekli, U., Sener, O., Deligiannidis, G. & Erdogdu, M. A. Hausdorff dimension, heavy tails, and generalization in neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 5138–5151 (2020).
Zhang, Y., Singh, A.K., Latham, P.E. & Saxe, A. Training dynamics of in-context learning in linear attention. Proc. 42nd International Conference on Machine Learning 267, 76047-76087 (PMLR, 2025).
Hopfield, J. J. Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 79, 2554–2558 (1982).
Google Scholar
Hinton, G. E. & Salakhutdinov, R. R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 313, 504–507 (2006).
Google Scholar
Hinton, G. E. & Sejnowski, T. J. in Parallel Distributed Processing, Volume 1: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition: Foundations (eds Rumelhart, D. E. & McClelland, J. L.) 282–317 (MIT Press, 1986).
Ambrogioni, L. In search of dispersed memories: generative diffusion models are associative memory networks. Entropy 26, 381 (2024).
Google Scholar
Pham, B. et al. Memorization to generalization: the emergence of diffusion models from associative memory. In NeurIPS 2024 Workshop on Scientific Methods for Understanding Deep Learning (2024).
Aksay, E., Gamkrelidze, G., Seung, H. S., Baker, R. & Tank, D. W. In vivo intracellular recording and perturbation of persistent activity in a neural integrator. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 184–193 (2001).
Google Scholar
Khona, M. & Fiete, I. R. Attractor and integrator networks in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 23, 744–766 (2022).
Google Scholar
Nair, A. et al. An approximate line attractor in the hypothalamus encodes an aggressive state. Cell 186, 178–193.e115 (2023).
Google Scholar
Zhang, K. Representation of spatial orientation by the intrinsic dynamics of the head-direction cell ensemble: a theory. J. Neurosci. 16, 2112–2126 (1996).
Google Scholar
Gardner, R. J. et al. Toroidal topology of population activity in grid cells. Nature 602, 123–128 (2022).
Google Scholar
Machens, C. K., Romo, R. & Brody, C. D. Flexible control of mutual inhibition: a neural model of two-interval discrimination. Science 307, 1121–1124 (2005).
Google Scholar
Durstewitz, D. Self-organizing neural integrator predicts interval times through climbing activity. J. Neurosci. 23, 5342–5353 (2003).
Google Scholar
Seung, H. S., Lee, D. D., Reis, B. Y. & Tank, D. W. Stability of the memory of eye position in a recurrent network of conductance-based model neurons. Neuron 26, 259–271 (2000).
Google Scholar
Mensh, B. D., Aksay, E., Lee, D. D., Seung, H. S. & Tank, D. W. Spontaneous eye movements in goldfish: oculomotor integrator performance, plasticity, and dependence on visual feedback. Vis. Res. 44, 711–726 (2004).
Google Scholar
Gallego, J. A., Perich, M. G., Miller, L. E. & Solla, S. A. Neural manifolds for the control of movement. Neuron 94, 978–984 (2017).
Google Scholar
Fransén, E., Tahvildari, B., Egorov, A. V., Hasselmo, M. E. & Alonso, A. A. Mechanism of graded persistent cellular activity of entorhinal cortex layer V neurons. Neuron 49, 735–746 (2006).
Google Scholar
Vinograd, A., Nair, A., Kim, J. H., Linderman, S. W. & Anderson, D. J. Causal evidence of a line attractor encoding an affective state. Nature 634, 910–918 (2024).
Google Scholar
Schmidt, D., Koppe, G., Monfared, Z., Beutelspacher, M. & Durstewitz, D. Identifying nonlinear dynamical systems with multiple time scales and long-range dependencies. In Proc. 9th International Conference on Learning Representations e1007263 (ICLR, 2021).
Hochreiter, S. & Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9, 1735–1780 (1997).
Google Scholar
Perko, L. Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems 7 (Springer, 2001).
Rabinovich, M. I., Huerta, R., Varona, P. & Afraimovich, V. S. Transient cognitive dynamics, metastability, and decision making. PLoS Comput. Biol. 4, e1000072 (2008).
Google Scholar
Rabinovich, M. I., Varona, P., Selverston, A. I. & Abarbanel, H. D. I. Dynamical principles in neuroscience. Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 1213–1265 (2006).
Google Scholar
Tsuda, I. Toward an interpretation of dynamic neural activity in terms of chaotic dynamical systems. Behav. Brain Sci. 24, 793–848 (2001).
Google Scholar
Tsuda, I. Chaotic itinerancy and its roles in cognitive neurodynamics. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 31, 67–71 (2015).
Google Scholar
Koch, D. et al. Ghost channels and ghost cycles guiding long transients in dynamical systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 133, 047202 (2024).
Google Scholar
Lapish, C. C., Balaguer-Ballester, E., Seamans, J. K., Phillips, A. G. & Durstewitz, D. Amphetamine exerts dose-dependent changes in prefrontal cortex attractor dynamics during working memory. J. Neurosci. 35, 10172 (2015).
Google Scholar
Komura, Y. et al. Retrospective and prospective coding for predicted reward in the sensory thalamus. Nature 412, 546–549 (2001).
Google Scholar
Wang, J., Narain, D., Hosseini, E. A. & Jazayeri, M. Flexible timing by temporal scaling of cortical responses. Nat. Neurosci. 21, 102–110 (2018).
Google Scholar
Spisak, T. & Friston, K. Self-orthogonalizing attractor neural networks emerging from the free energy principle. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2505.22749 (2025).
Rouse, N. A. & Daltorio, K. A. Visualization of stable heteroclinic channel-based movement primitives. IEEE Rob. Autom. Lett. 6, 2343–2348 (2021).
Google Scholar
Mengers, N., Rouse, N. & Daltorio, K. A. Stable heteroclinic channels for controlling a simulated aquatic serpentine robot in narrow crevices. Front. Electron. 6, 1507644 (2025).
Google Scholar
Durstewitz, D. & Seamans, J. K. The computational role of dopamine D1 receptors in working memory. Neural Netw. 15, 561–572 (2002).
Google Scholar
Chahine, M. et al. Robust flight navigation out of distribution with liquid neural networks. Sci. Rob. 8, eadc8892 (2023).
Google Scholar
Baronig, M., Ferrand, R., Sabathiel, S. & Legenstein, R. Advancing spatio-temporal processing through adaptation in spiking neural networks. Nat. Commun. 16, 5776 (2025).
Google Scholar
Wang, G. et al. Hierarchical reasoning model. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2506.21734 (2025).
Doya, K. Bifurcations in the learning of recurrent neural networks. In Proc. 1992 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems Vol. 6, 2777–2780 (IEEE, 1992).
Beggs, J. M. & Plenz, D. Neuronal avalanches in neocortical circuits. J. Neurosci. 23, 11167–11177 (2003).
Google Scholar
Bertschinger, N. & Natschläger, T. Real-time computation at the edge of chaos in recurrent neural networks. Neural Comput. 16, 1413–1436 (2004).
Google Scholar
Shew, W. L., Yang, H., Petermann, T., Roy, R. & Plenz, D. Neuronal avalanches imply maximum dynamic range in cortical networks at criticality. J. Neurosci. 29, 15595–15600 (2009).
Google Scholar
Cocchi, L., Gollo, L. L., Zalesky, A. & Breakspear, M. Criticality in the brain: a synthesis of neurobiology, models and cognition. Prog. Neurobiol. 158, 132–152 (2017).
Google Scholar
Murray, J. D. et al. A hierarchy of intrinsic timescales across primate cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 1661–1663 (2014).
Google Scholar
Stemmler, M. & Koch, C. How voltage-dependent conductances can adapt to maximize the information encoded by neuronal firing rate. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 521–527 (1999).
Google Scholar
Zhong, L. et al. Unsupervised pretraining in biological neural networks. Nature 644, 741–748 (2025).
Citri, A. & Malenka, R. C. Synaptic Plasticity: Multiple Forms, Functions, and Mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 33, 18–41 (2008).
Google Scholar
Holtmaat, A. & Svoboda, K. Experience-dependent structural synaptic plasticity in the mammalian brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10, 647–658 (2009).
Google Scholar
Fu, M. & Zuo, Y. Experience-dependent structural plasticity in the cortex. Trends Neurosci. 34, 177–187 (2011).
Google Scholar
Sagi, Y. et al. Learning in the fast lane: new insights into neuroplasticity. Neuron 73, 1195–1203 (2012).
Google Scholar
Ioffe, S. & Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proc. 32nd International conference on machine learning Vol. 37, 448–456 (PMLR, 2015).
Salimans, T. & Kingma, D. P. Weight normalization: a simple reparameterization to accelerate training of deep neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 29, 901–909 (2016).
Turrigiano, G. G., Leslie, K. R., Desai, N. S., Rutherford, L. C. & Nelson, S. B. Activity-dependent scaling of quantal amplitude in neocortical neurons. Nature 391, 892–896 (1998).
Google Scholar
Kaplanis, C., Shanahan, M. & Clopath, C. Continual reinforcement learning with complex synapses. In Proc. 35th International Conference on Machine Learning 2497–2506 (PMLR, 2018).
Laborieux, A., Ernoult, M., Hirtzlin, T. & Querlioz, D. Synaptic metaplasticity in binarized neural networks. Nat. Commun. 12, 2549 (2021).
Google Scholar
Schultz, W. Dopamine reward prediction-error signalling: a two-component response. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 183–195 (2016).
Google Scholar
Doya, K. Metalearning and neuromodulation. Neural Netw. 15, 495–506 (2002).
Google Scholar
Izhikevich, E. M. Solving the distal reward problem through linkage of stdp and dopamine signaling. Cereb. Cortex 17, 2443–2452 (2007).
Google Scholar
Huttenlocher, P. R. & Dabholkar, A. S. Regional differences in synaptogenesis in human cerebral cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 387, 167–178 (1997).
Google Scholar
Hensch, T. K. Critical period regulation. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 27, 549–579 (2004).
Google Scholar
Ba, J., Hinton, G. E., Mnih, V., Leibo, J. Z. & Ionescu, C. Using fast weights to attend to the recent past. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 29, 4331–4339 (2016).
Hofmann, M., Becker, M. F. P., Tetzlaff, C. & Mäder, P. Concept transfer of synaptic diversity from biological to artificial neural networks. Nat. Commun. 16, 5112 (2025).
Google Scholar
Benna, M. K. & Fusi, S. Computational principles of synaptic memory consolidation. Nat. Neurosci. 19, 1697–1706 (2016).
Google Scholar
Ralambomihanta, T. R. et al. Learning from the past with cascading eligibility traces. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2506.14598 (2025).
Wang, J. X. Meta-learning in natural and artificial intelligence. Curr. Opin. Syst. Biol. 38, 90–95 (2021).
Ostapenko, O., Puscas, M., Klein, T., Jahnichen, P. & Nabi, M. Learning to remember: a synaptic plasticity driven framework for continual learning. In Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 11321–11329 (IEEE, 2019).
Ben-Iwhiwhu, E., Nath, S., Pilly, P. K., Kolouri, S. & Soltoggio, A. Lifelong reinforcement learning with modulating masks. Trans. Mach. Learn. Res. https://openreview.net/forum?id=V7tahqGrOq (2023).
Miconi, T., Stanley, K. & Clune, J. Differentiable plasticity: training plastic neural networks with backpropagation. In Proc. 35th International Conference on Machine Learning Vol. 80, 3559–3568 (PMLR, 2018).
Shervani-Tabar, N. & Rosenbaum, R. Meta-learning biologically plausible plasticity rules with random feedback pathways. Nat. Commun. 14, 1805 (2023).
Google Scholar
Yu, Y., Jin, Y., Xiao, Y. & Yan, Y. A Recurrent spiking network with hierarchical intrinsic excitability modulation for schema learning. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2501.14539 (2025).
Bengio, Y., Louradour, J., Collobert, R. & Weston, J. Curriculum learning. In Proc. 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning 41–48 (Association for Computing Machinery, 2009).
Brock, A., Lim, T., Ritchie, J. M. & Weston, N. J. FreezeOut: accelerate training by progressively freezing layers. In 10th NIPS Workshop on Optimization for Machine Learning Vol. 10 (NIPS, 2017).
Sorrenti, A. et al. Selective freezing for efficient continual learning. In 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW) 3542–3551 (IEEE, 2023).
Shi, T., Wu, Y., Song, L., Zhou, T. & Zhao, J. Efficient reinforcement finetuning via adaptive curriculum learning. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2504.05520 (2025).
Tolman, E. C. Purposive Behavior in Animals and Men (Appleton-Century-Crofts, 1932).
Tolman, E. C. & Honzik, C. H. Introduction and removal of reward, and maze performance in rats. Univ. Calif. Pub. Psychol. 4, 257–275 (1930).
Ke, N. R. et al. Sparse attentive backtracking: temporal credit assignment through reminding. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 31, 7651–7662 (2018).
McClelland, J. L., McNaughton, B. L. & O’Reilly, R. C. Why there are complementary learning systems in the hippocampus and neocortex: insights from the successes and failures of connectionist models of learning and memory. Psychol. Rev. 102, 419 (1995).
Google Scholar
Sun, W., Advani, M., Spruston, N., Saxe, A. & Fitzgerald, J. E. Organizing memories for generalization in complementary learning systems. Nat. Neurosci. 26, 1438–1448 (2023).
Google Scholar
Samborska, V., Butler, J. L., Walton, M. E., Behrens, T. E. J. & Akam, T. Complementary task representations in hippocampus and prefrontal cortex for generalizing the structure of problems. Nat. Neurosci. 25, 1314–1326 (2022).
Google Scholar
Moscovitch, M., Cabeza, R., Winocur, G. & Nadel, L. Episodic memory and beyond: the hippocampus and neocortex in transformation. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 67, 105–134 (2016).
Google Scholar
Treves, A. & Rolls, E. T. Computational analysis of the role of the hippocampus in memory. Hippocampus 4, 374–391 (1994).
Google Scholar
Kumaran, D., Hassabis, D. & McClelland, J. L. What learning systems do intelligent agents need? Complementary learning systems theory updated. Trends Cogn. Sci. 20, 512–534 (2016).
Google Scholar
Wilson, M. A. & McNaughton, B. L. Reactivation of hippocampal ensemble memories during sleep. Science 265, 676–679 (1994).
Google Scholar
Foster, D. J. Replay comes of age. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 40, 581–602 (2017).
Google Scholar
Rolnick, D., Ahuja, A., Schwarz, J., Lillicrap, T. & Wayne, G. Experience replay for continual learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 32, 350–360 (2019).
Shi, Q. et al. Hybrid neural networks for continual learning inspired by corticohippocampal circuits. Nat. Commun. 16, 1272 (2025).
Google Scholar
Du, J. -l, Wei, H. -p, Wang, Z. -r, Wong, S. T. & Poo, M. -m Long-range retrograde spread of LTP and LTD from optic tectum to retina. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 18890–18896 (2009).
Google Scholar
Zhang, T. et al. Self-backpropagation of synaptic modifications elevates the efficiency of spiking and artificial neural networks. Sci. Adv. 7, eabh0146 (2021).
Google Scholar
Kohonen, T. Self-organized formation of topologically correct feature maps. Biol. Cybern. 43, 59–69 (1982).
Google Scholar
Kohonen, T. Analysis of a simple self-organizing process. Biol. Cybern. 44, 135–140 (1982).
Google Scholar
Oja, E. Simplified neuron model as a principal component analyzer. J. Math. Biol. 15, 267–273 (1982).
Google Scholar
Oja, E. & Karhunen, J. On stochastic approximation of the eigenvectors and eigenvalues of the expectation of a random matrix. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 106, 69–84 (1985).
Google Scholar
Hertz, J. A., Krogh, A. & Palmer, R. G. Introduction To The Theory Of Neural Computation, I. (Westview Press, 1991).
Kuriscak, E., Marsalek, P., Stroffek, J. & Toth, P. G. Biological context of Hebb learning in artificial neural networks, a review. Neurocomputing 152, 27–35 (2015).
Google Scholar
Schmidgall, S. et al. Brain-inspired learning in artificial neural networks: a review. APL Mach. Learn. 2, 021501 (2024).
Google Scholar
Drew, P. J. & Abbott, L. F. Extending the effects of spike-timing-dependent plasticity to behavioral timescales. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 8876–8881 (2006).
Google Scholar
Soltoggio, A. Short-term plasticity as cause–effect hypothesis testing in distal reward learning. Biol. Cybern. 109, 75–94 (2015).
Google Scholar
Lu, S. & Sengupta, A. Deep unsupervised learning using spike-timing-dependent plasticity. Neuromorphic Comput. Eng. 4, 024004 (2024).
Google Scholar
Apolinario, M. P. E. & Roy, K. S-TLLR: STDP-inspired temporal local learning rule for spiking neural networks. Trans. Mach. Learn. Res. https://openreview.net/forum?id=vlQ56aWJhl (2025).
Rahman, N. A. & Yusoff, N. Modulated spike-time dependent plasticity (STDP)-based learning for spiking neural network (SNN): a review. Neurocomputing 618, 129170 (2025).
Google Scholar
Kudithipudi, D. et al. Neuromorphic computing at scale. Nature 637, 801–812 (2025).
Google Scholar
Bittner, K. C. et al. Conjunctive input processing drives feature selectivity in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 1133–1142 (2015).
Google Scholar
Qian, F. K., Li, Y. & Magee, J. C. Mechanisms of experience-dependent place-cell referencing in hippocampal area CA1. Nat. Neurosci. 28, 1486–1496 (2025).
Google Scholar
Pang, R. & Recanatesi, S. A non-Hebbian code for episodic memory. Sci. Adv. 11, eado4112 (2025).
Google Scholar
Fusi, S., Asaad, W. F., Miller, E. K. & Wang, X.-J. A neural circuit model of flexible sensorimotor mapping: learning and forgetting on multiple timescales. Neuron 54, 319–333 (2007).
Google Scholar
Russo, E. & Durstewitz, D. Cell assemblies at multiple time scales with arbitrary lag constellations. eLife 6, e19428 (2017).
Google Scholar
Cavanagh, S. E., Hunt, L. T. & Kennerley, S. W. A diversity of intrinsic timescales underlie neural computations. Front. Neural Circuits 14, 615626 (2020).
Google Scholar
Gao, R., van den Brink, R. L., Pfeffer, T. & Voytek, B. Neuronal timescales are functionally dynamic and shaped by cortical microarchitecture. eLife 9, e61277 (2020).
Google Scholar
Zijlmans, M. et al. High-frequency oscillations as a new biomarker in epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 71, 169–178 (2012).
Google Scholar
Spaak, E., de Lange, F. P. & Jensen, O. Local entrainment of alpha oscillations by visual stimuli causes cyclic modulation of perception. J. Neurosci. 34, 3536–3544 (2014).
Google Scholar
Momtaz, S. & Bidelman, G. M. Effects of stimulus rate and periodicity on auditory cortical entrainment to continuous sounds. eneuro 11, ENEURO.0027-0023.2024 (2024).
Google Scholar
Durstewitz, D. Neural representation of interval time. NeuroReport 15, 745–749 (2004).
Google Scholar
Rosenberg, M., Zhang, T., Perona, P. & Meister, M. Mice in a labyrinth show rapid learning, sudden insight, and efficient exploration. eLife 10, e66175 (2021).
Google Scholar
Zipser, D. Recurrent network model of the neural mechanism of short-term active memory. Neural Comput. 3, 179–193 (1991).
Google Scholar
Rajalingham, R., Piccato, A. & Jazayeri, M. Recurrent neural networks with explicit representation of dynamic latent variables can mimic behavioral patterns in a physical inference task. Nat. Commun. 13, 5865 (2022).
Google Scholar
Mante, V., Sussillo, D., Shenoy, K. V. & Newsome, W. T. Context-dependent computation by recurrent dynamics in prefrontal cortex. Nature 503, 78–84 (2013).
Google Scholar
Gu, A. & Dao, T. Mamba: linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2312.00752 (2023).
Bulatov, A., Kuratov, Y. & Burtsev, M. Recurrent memory transformer. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 11079–11091 (2022).
Hutchins, D., Schlag, I., Wu, Y., Dyer, E. & Neyshabur, B. Block-recurrent transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 33248–33261 (2022).
Kriegeskorte, N. Deep neural networks: a new framework for modeling biological vision and brain information processing. Annu. Rev. Vision Sci. 1, 417–446 (2015).
Google Scholar
Kumar, S. et al. Shared functional specialization in transformer-based language models and the human brain. Nat. Commun. 15, 5523 (2024).
Google Scholar
Whittington, J. C., Warren, J. & Behrens, T. E. Relating transformers to models and neural representations of the hippocampal formation. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2112.04035 (2021).
Miikkulainen, R. Neuroevolution insights into biological neural computation. Science 387, eadp7478 (2025).
Google Scholar
Durstewitz, D., Koppe, G. & Thurm, M. I. Reconstructing computational system dynamics from neural data with recurrent neural networks. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 693–710 (2023).
Google Scholar
Brenner, M., Weber, E., Koppe, G. & Durstewitz, D. Learning interpretable hierarchical dynamical systems models from time series data. In Proc. 13th International Conference on Learning Representations 1–37 (ICLR, 2025).
Brenner, M., Hess, F., Koppe, G. & Durstewitz, D. Integrating multimodal data for joint generative modeling of complex dynamics. In Proc. 41st International Conference on Machine Learning Vol. 235, 4482–4516 (PMLR, 2024).
Glaser, J., Whiteway, M., Cunningham, J. P., Paninski, L. & Linderman, S. Recurrent switching dynamical systems models for multiple interacting neural populations. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 14867–14878 (2020).
Pals, M., Sağtekin, A. E., Pei, F., Gloeckler, M. & Macke, J. H. Inferring stochastic low-rank recurrent neural networks from neural data. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 37, 18225–18264 (2024).
Hess, F., Monfared, Z., Brenner, M. & Durstewitz, D. Generalized teacher forcing for learning chaotic dynamics. In Proc. 11th International Conference on Machine Learning 13017–13049 (ICML, 2023).
Platt, J. A., Penny, S. G., Smith, T. A., Chen, T.-C. & Abarbanel, H. D. I. Constraining chaos: enforcing dynamical invariants in the training of reservoir computers. Chaos 33, 103107 (2023).
Google Scholar
Lim, S. et al. Inferring learning rules from distributions of firing rates in cortical neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 1804–1810 (2015).
Google Scholar
Mehta, Y. et al. Model based inference of synaptic plasticity rules. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 37, 48519–48540 (2024).
Chen, S., Yang, Q. & Lim, S. Efficient inference of synaptic plasticity rule with Gaussian process regression. iScience 26, 106182 (2023).
Google Scholar
Don’t miss more hot News like this! Click here to discover the latest in AI news!
2025-11-28 00:00:00