Building an A2A-Compliant Random Number Agent: A Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing the Low-Level Executor Pattern with Python
The agent to the agent (A2A) is a new standard of Google that enables artificial intelligence agents-not to achieve their business framework or their primary developer-from communication and cooperation smoothly. It works using uniform messages and agent cards (describing what the agent can do), and task -based implementation, allowing agents to interact via HTTP without the logic of dedicated integration. The A2A makes it easy to build multi -developed developed agents by extracting communications.
In this tutorial, we will implement a simple demo agent that restores a random number, helping you to understand the basic structure and flow of A2A protocol through practical software instructions.
Preparation of dependencies
We will first prepare our environment and start installing the UV package manager. For Mac or Linux:
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh For Windows (PowerShell):
powershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex"Then we will create a new project guide and prepare it with UV
uv init a2a-demo
cd a2a-demoWe can now create and activate a virtual environment. For Mac or Linux:
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activateFor Windows:
uv venv
.venv\Scripts\activateWe will now install the required dependencies
uv add a2a-sdk python-a2a uvicornImplementation of basic blocks
Agent_Executor.PY)
In this step, we implement the basic logic of our agent by creating Agent Executor, responsible for dealing with the requests received and returning to A2A format. the Randomnumbegenetexecutor Simple wrap random This generates a random number between 1 and 100. When the request comes, the implementation method requires the logic of the agent and pays the result to the upcoming awaiting list as a uniform A2A. This setting is the logic of the back interface with which A2A customers can interact with. verify Complete symbols on Jabbap
import random
from a2a.server.agent_execution import AgentExecutor
from a2a.server.agent_execution.context import RequestContext
from a2a.server.events.event_queue import EventQueue
from a2a.utils import new_agent_text_message
from pydantic import BaseModel
class RandomNumberAgent(BaseModel):
"""Generates a random number between 1 and 100"""
async def invoke(self) -> str:
number = random.randint(1, 100)
return f"Random number generated: {number}"
class RandomNumberAgentExecutor(AgentExecutor):
def __init__(self):
self.agent = RandomNumberAgent()
async def execute(self, context: RequestContext, event_queue: EventQueue):
result = await self.agent.invoke()
await event_queue.enqueue_event(new_agent_text_message(result))
async def cancel(self, context: RequestContext, event_queue: EventQueue):
raise Exception("Cancel not supported")Preparation of A2A server and agent card (MAIN.PY)
In this section, we define the descriptive data that describes what our agent can do – and this is called The agent card. Think about it as a work card for the agent, containing information such as its name, description, available skills, input/output types, and version.
We also record the agent’s skills, which determine the type of tasks that he can handle. In our case, it includes the skill of creating a random number, which was properly marked and with an example of an example.
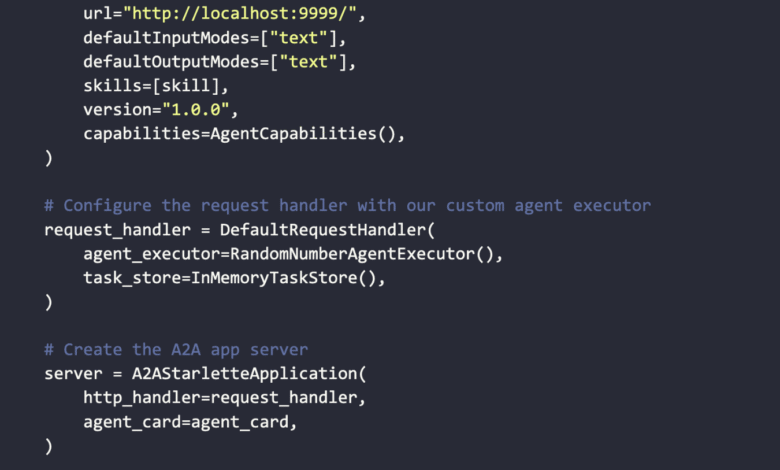
Once the descriptive data is ready, we create the A2A server using A2ASTARLTAEPLOCION. We offer the agent card and connect it to the logic of our dedicated agent using a DefautrequesthandlerWho uses Randomnumbegenetexecutor We implemented it earlier. Finally, we turn on the server using Uvicorn so that the agent can start listening to the A2A messages on the port 9999.
This setting enables our agent to receive and process uniform A2A messages and respond in an organized manner – following the A2A protocol. verify Complete symbols on Jabbap
import uvicorn
from a2a.server.apps import A2AStarletteApplication
from a2a.server.request_handlers import DefaultRequestHandler
from a2a.server.tasks import InMemoryTaskStore
from a2a.types import AgentCapabilities, AgentCard, AgentSkill
from agent_executor import RandomNumberAgentExecutor
def main():
# Define the skill metadata
skill = AgentSkill(
id="random_number",
name="Random Number Generator",
description="Generates a random number between 1 and 100",
tags=["random", "number", "utility"],
examples=["Give me a random number", "Roll a number", "Random"],
)
# Define the agent metadata
agent_card = AgentCard(
name="Random Number Agent",
description="An agent that returns a random number between 1 and 100",
url="http://localhost:9999/",
defaultInputModes=["text"],
defaultOutputModes=["text"],
skills=[skill],
version="1.0.0",
capabilities=AgentCapabilities(),
)
# Configure the request handler with our custom agent executor
request_handler = DefaultRequestHandler(
agent_executor=RandomNumberAgentExecutor(),
task_store=InMemoryTaskStore(),
)
# Create the A2A app server
server = A2AStarletteApplication(
http_handler=request_handler,
agent_card=agent_card,
)
# Run the server
uvicorn.run(server.build(), host="0.0.0.0", port=9999)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Interacting with the agent using A2ACLIENT (Client.Py)
Next, we create the customer who will interact with our A2A agent. This client text program performs three main tasks:
- Bring the agent card: We start to solve public agent data using A2ACARDRESOLVER. This brings the Agent.json file from the known end point. -Well, which contains basic details such as the name of the agent, description, skills and communication capabilities.
- Conside the A2A customerUsing Agentted Card, we have prepared A2ACLIENT, which takes into account the connection protocol. This customer will be responsible for sending organized messages to the agent and receiving responses.
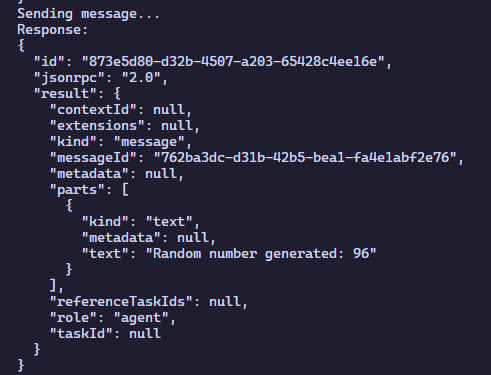
Send a message and receive a response: We build a message with the text “Give me a random number” using the A2A message structure (the message, part, Textpart). The message is sent as part of the Sendmessgerequest, which wraps it with a unique request. Once the message is sent, the agent processes it and responds with a random number created, which is then printed in JSON format. verify Complete symbols on Jabbap
import uuid
import httpx
from a2a.client import A2ACardResolver, A2AClient
from a2a.types import (
AgentCard,
Message,
MessageSendParams,
Part,
Role,
SendMessageRequest,
TextPart,
)
PUBLIC_AGENT_CARD_PATH = "/.well-known/agent.json"
BASE_URL = "http://localhost:9999"
async def main() -> None:
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as httpx_client:
# Fetch the agent card
resolver = A2ACardResolver(httpx_client=httpx_client, base_url=BASE_URL)
try:
print(f"Fetching public agent card from: {BASE_URL}{PUBLIC_AGENT_CARD_PATH}")
agent_card: AgentCard = await resolver.get_agent_card()
print("Agent card fetched successfully:")
print(agent_card.model_dump_json(indent=2))
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error fetching public agent card: {e}")
return
# Initialize A2A client with the agent card
client = A2AClient(httpx_client=httpx_client, agent_card=agent_card)
# Build message
message_payload = Message(
role=Role.user,
messageId=str(uuid.uuid4()),
parts=[Part(root=TextPart(text="Give me a random number"))],
)
request = SendMessageRequest(
id=str(uuid.uuid4()),
params=MessageSendParams(message=message_payload),
)
# Send message
print("Sending message...")
response = await client.send_message(request)
# Print response
print("Response:")
print(response.model_dump_json(indent=2))
if __name__ == "__main__":
import asyncio
asyncio.run(main())
Run the agent and inquire about himself
For our A2A setting test, we will start running the agent server. This is done by implementing the MAIN.PY file, which prepares the agent, displays his agent card, and listens to the requests received at the port 9999. Check out Complete symbols on Jabbap
Once the agent runs, we will move to the customer’s text. The customer will attend the agent’s definition data, send an organized inquiry using the A2A protocol, and receive a response. In our case, query is a simple message like “Give me a random number”, and the agent will return a number between 1 and 100.
verify Complete symbols on Jabbap. All the credit for this research goes to researchers in this project. Also, do not hesitate to follow us twitter And do not forget to join 100K+ ML Subreddit And subscribe to Our newsletter.

I am a graduate of civil engineering (2022) from Islamic Melia, New Delhi, and I have a strong interest in data science, especially nervous networks and their application in various fields.

Don’t miss more hot News like this! AI/" target="_blank" rel="noopener">Click here to discover the latest in AI news!
2025-06-21 07:19:00




