Deadly ‘Wet-Bulb’ Temperatures Are Smothering the Eastern U.S.
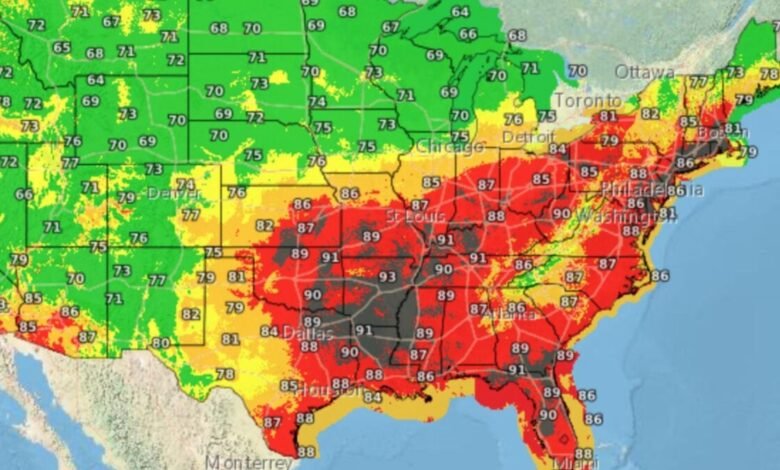
The Repressive Hit dome in the eastern United States acquired this week, prompting the national weather service (NWS) to issue heat warnings of about 170 million Americans. What is more mud is that extreme humidity makes high temperatures feel hotter.
Severe heat and moisture make a fatal group. The human body reduces its temperature by sweating, and when the sweat evaporates, the surface of the skin cools. Moisture slows down this process, which increases the risk of developing heat. To extrapolate the physiological effect combined with heat and humidity, meteorologists look at wet bopy. This measurement mainly represents the amount of thermal stress that the body faces under warm hot conditions. It is also a crucial measure to understand the ability to survive in the variable climate.
“The wet urine temperature is literally the temperature of the wet heat bulb, which is traditionally measured by placing a small wet sock at the end of the heat scale,” said David Rumbs, a professor of Earth sciences and planets at the University of California-Birkley. Similar to a person sweating, the slow wet heat scale cools by evaporation of water, “but the wet bipping scale is not like a person in some important methods,” he explained.
Humans generate body temperature, which must be watered in the air. “Therefore, everything else is equal, the person who smells of sweat will be warmer than a wet lamp,” said Rumbs. When the wet hybrid temperature approaches 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit (37 ° C)-the average human body temperature-is very difficult to maintain a safe internal temperature. He explained that this may lead to a severe disease associated with heat or even death.
Experts have long believed that the wet polypillary temperature is 35 ° C (equal to 95 degrees Fahrenheit at 100 % moisture or 115 degrees Fahrenheit at 50 % moisture) the threshold that the human body no longer was to cool itself. However, in recent years, researchers have found evidence that this threshold is much lower.
“Based on our research, the temperature of the wet lamp is about 87 degrees Fahrenheit [30.6 degrees Celsius] “The 100 % humidity is the decisive threshold that humans cannot maintain a stable basic temperature if they are exposed to these conditions for hours at one time,” Cat Fischer, a doctorate candidate at the Human Thermal Laboratory at Pennsylvania State University, told Gizmodo in an email.
Taking into account the wet diox temperature with the air temperature, wind speed, cloud cover and sunscreen, meteorologists give the wet spherical temperature (WBGT), which is a comprehensive measure of thermal stress in direct sunlight. On Tuesday, July 29, NWS reported the values of WBGT in the 1980s to the 90s Fahrenheit (the top of the twenties to the mid -thirties) across most of the eastern United States, especially in the southeast and central.
WBGT values are higher than 90 degrees Fahrenheit (32 ° C) extremes and can stimulate heat stress in only 15 minutes when working or exercising in direct sunlight, according to NWS. Weather officials expect these circumstances to continue until Wednesday, July 29, before the Heat dome was dissipated later in the week.
In the long run, the dangerous wet temperature events here to stay. “The global warming caused by a person leads the temperature of wet temperatures, which causes even healthy people near the physiological limit. This limit is real.” He explained that the human body is unable physiologically to hunt wet temperatures around or higher than its internal temperature.
With the high temperature of the air, it can carry more moisture, which increases the frequency and intensity of severe wet temperatures. Climate models indicate that certain regions of the world can see humidity temperatures regularly at 95 degrees Fahrenheit (35 ° C) during the next thirty to 50 years, according to NASA. In the United States, the Middle West countries like Arkansas, Missouri and Iowa are likely to reach a critical wet temperature within 50 years.
“For 300,000 years of our genus, there was no need to tolerate wet temperatures because it is likely that it did not happen as a natural part of the weather throughout that time,” said Rums. “Global warming changes this, quickly.”
Severe heat is already more dangerous, bloody weather in US data from diseases and prevention control centers (CDC) that approximately 2000 Americans die of heat related reasons annually, according to ABC News reports. Some experts believe that the death toll has been reduced. Understanding the limits of human survival in a warmer world is literally a matter of life or death. There is an urgent need to adapt infrastructure, public health systems and intense heat response standards to the changing climate.
Don’t miss more hot News like this! Click here to discover the latest in Technology news!
2025-07-30 00:00:00




