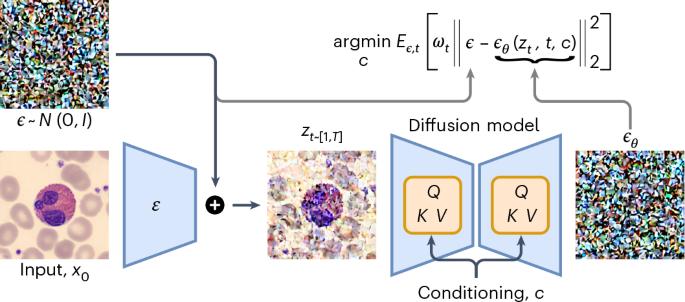
Deep generative classification of blood cell morphology
Bain, B. J. Blood Cells: A Practical Guide (John Wiley & Sons, 2021).
Kratz, A. et al. Digital morphology analyzers in hematology: ICSH review and recommendations. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 41, 437–447 (2019).
Google Scholar
Buttarello, M. & Plebani, M. Automated blood cell counts: state of the art. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 130, 104–116 (2008).
Google Scholar
van de Geijn, G.-J. et al. Leukoflow: multiparameter extended white blood cell differentiation for routine analysis by flow cytometry. Cytometry A 79A, 694–706 (2011).
Google Scholar
Metter, G. E. et al. Morphological subclassification of follicular lymphoma: variability of diagnoses among hematopathologists, a collaborative study between the repository center and pathology panel for lymphoma clinical studies. J. Clin. Oncol. 3, 25–38 (1985).
Google Scholar
Claro, M. et al. Convolution neural network models for acute leukemia diagnosis. In Proc. IEEE International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing (IWSSIP) (eds Paiva, A. C. et al.) 63–68 (IEEE, 2020).
Pansombut, T., Wikaisuksakul, S., Khongkraphan, K. & Phon-On, A. Convolutional neural networks for recognition of lymphoblast cell images. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2019, 7519603 (2019).
Google Scholar
Hehr, M. et al. Explainable AI identifies diagnostic cells of genetic AML subtypes. PLOS Digit. Health 2, e0000187 (2023).
Google Scholar
Routt, A. H., Yang, N., Piety, N. Z., Lu, M. & Shevkoplyas, S. S. Deep ensemble learning enables highly accurate classification of stored red blood cell morphology. Sci. Rep. 13, 3152 (2023).
Google Scholar
Doan, M. et al. Objective assessment of stored blood quality by deep learning. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117, 21381–21390 (2020).
Google Scholar
Matek, C., Krappe, S., Münzenmayer, C., Haferlach, T. & Marr, C. Highly accurate differentiation of bone marrow cell morphologies using deep neural networks on a large image data set. Blood 138, 1917–1927 (2021).
Google Scholar
Yoon, J. S., Oh, K., Shin, Y., Mazurowski, M. A. & Suk, H.-I. Domain generalization for medical image analysis: a review. Proc. IEEE 112, 1583–1609 (2024).
Google Scholar
Koh, P. W. et al. Wilds: a benchmark of in-the-wild distribution shifts. In Proc. 38th International Conference on Machine Learning (eds Meila, M. & Zhang, T.) 5637–5664 (PMLR, 2021).
Holzinger, A., Langs, G., Denk, H., Zatloukal, K. & Müller, H. Causability and explainability of artificial intelligence in medicine. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 9, e1312 (2019).
Google Scholar
Rudin, C. Stop explaining black box machine learning models for high stakes decisions and use interpretable models instead. Nat. Mach. Intell. 1, 206–215 (2019).
Google Scholar
Kazerouni, A. et al. Diffusion models in medical imaging: a comprehensive survey. Med. Image Anal. 88, 102846 (2023).
Google Scholar
Begoli, E., Bhattacharya, T. & Kusnezov, D. The need for uncertainty quantification in machine-assisted medical decision making. Nat. Mach. Intell. 1, 20–23 (2019).
Google Scholar
Asghar, R., Kumar, S., Shaukat, A. & Hynds, P. Classification of white blood cells (leucocytes) from blood smear imagery using machine and deep learning models: a global scoping review. PLoS ONE 19, e0292026 (2024).
Google Scholar
Kumar, R., Kumbharkar, P., Vanam, S. & Sharma, S. Medical images classification using deep learning: a survey. Multimed. Tools Appl. 83, 19683–19728 (2024).
Google Scholar
Li, A. C., Kumar, A. & Pathak, D. Generative classifiers avoid shortcut solutions. In Proc. ICML 2024 Workshop on Structured Probabilistic Inference & Generative Modeling (ICML, 2024).
Chen, H. et al. Robust classification via a single diffusion model. In Proc. 41st International Conference on Machine Learning (eds Salakhutdinov, R. et al.) 6643–6665 (PMLR, 2024).
Clark, K. & Jaini, P. Text-to-image diffusion models are zero shot classifiers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 36, 58921–58937 (2024).
Li, A. C., Prabhudesai, M., Duggal, S., Brown, E. & Pathak, D. Your diffusion model is secretly a zero-shot classifier. In Proc. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision 2206–2217 (IEEE, 2023).
Rombach, R., Blattmann, A., Lorenz, D., Esser, P. & Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (eds Dana, K. et al.) 10684–10695 (IEEE, 2022).
Kouzehkanan, Z. M. et al. A large dataset of white blood cells containing cell locations and types, along with segmented nuclei and cytoplasm. Sci. Rep. 12, 1123 (2022).
Google Scholar
Acevedo, A. et al. A dataset of microscopic peripheral blood cell images for development of automatic recognition systems. Data Br. 30, 105474 (2020).
Google Scholar
Bodzas, A., Kodytek, P. & Zidek, J. A high-resolution large-scale dataset of pathological and normal white blood cells. Sci. Data 10, 466 (2023).
Google Scholar
Kendall, A. & Gal, Y. What uncertainties do we need in Bayesian deep learning for computer vision? Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30, 2871 (2017).
Ovadia, Y. et al. Can you trust your model’s uncertainty? Evaluating predictive uncertainty under dataset shift. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 32, 13969–13980 (2019).
Selvaraju, R. R. et al. Grad-CAM: visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proc. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (eds Cucchiara, R. et al.) 618–626 (IEEE, 2017).
Ribeiro, M. T., Singh, S. & Guestrin, C. ‘Why should I trust you?’ Explaining the predictions of any classifier. In Proc. 22nd ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (eds Krishnapuram, B. et al.) 1135–1144 (ACM, 2016).
Deng, J. et al. ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proc. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (eds Essa, I. et al.) 248–255 (IEEE, 2009).
Shanbhag, A. S. et al. Just leaf it: accelerating diffusion classifiers with hierarchical class pruning. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.12073 (2024).
Pombo, G. et al. Equitable modelling of brain imaging by counterfactual augmentation with morphologically constrained 3D deep generative models. Med. Image Anal. 84, 102723 (2023).
Google Scholar
Paulson, E. A sequential procedure for selecting the population with the largest mean from k normal populations. Ann. Math. Stat. 35, 174–180 (1964).
Even-Dar, E., Mannor, S. & Mansour, Y. PAC bounds for multi-armed bandit and Markov decision processes. In Proc. 15th Annual Conference on Computational Learning Theory (COLT 2002) (eds Kivinen, J. & Sloan, R. H.) 255–270 (Springer, 2002).
Firat, H. Ü. Classification of microscopic peripheral blood cell images using multibranch lightweight CNN-based model. Neural Comput. Appl. 36, 1599–1620 (2024).
Google Scholar
Abou Ali, M., Dornaika, F. & Arganda-Carreras, I. Blood cell revolution: unveiling 11 distinct types with ‘naturalize’ augmentation. Algorithms 16, 562 (2023).
Google Scholar
Kalweit, G. et al. Unsupervised feature extraction from a foundation model zoo for cell similarity search in oncological microscopy across devices. In Proc. ICML 2024 Workshop on Foundation Models in the Wild (ICML, 2024).
Garcia Llagostera, A. Developing a Scalable and Privacy-Preserving Deep Learning Model for the Classification of Peripheral Blood Cell Images. Master’s thesis, Univ. Oberta de Catalunya (2024).
Zhang, R. et al. RCMNet: a deep learning model assists CAR-T therapy for leukemia. Comput. Biol. Med. 150, 106084 (2022).
Long, F., Peng, J.-J., Song, W., Xia, X. & Sang, J. BloodCaps: a capsule network based model for the multiclassification of human peripheral blood cells. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 202, 105972 (2021).
Google Scholar
Rubin, R., Anzar, S. M., Panthakkan, A. & Mansoor, W. Transforming healthcare: Raabin white blood cell classification with deep vision transformer. In Proc. 6th International Conference on Signal Processing and Information Security (ICSPIS 2023) (eds Beheshti, A. & Mukhtar, H.) 212–217 (IEEE, 2023).
Gescheider, G. A. Psychophysics: The Fundamentals 3rd edn (Psychology Press, 1997).
Schütt, H. H., Harmeling, S., Macke, J. H. & Wichmann, F. A. Painfree and accurate Bayesian estimation of psychometric functions for (potentially) overdispersed data. Vision Res. 122, 105–123 (2016).
Google Scholar
Mah, Y.-H., Jager, R., Kennard, C., Husain, M. & Nachev, P. A new method for automated high-dimensional lesion segmentation evaluated in vascular injury and applied to the human occipital lobe. Cortex 56, 51–63 (2014).
Google Scholar
Rieck, K. & Laskov, P. Detecting unknown network attacks using language models. In Proc. 3rd International Conference on Detection of Intrusions and Malware & Vulnerability Assessment (DIMVA 2006) (eds Büschkes, R. & Laskov, P.) 74–90 (Springer, 2006).
Rezatofighi, S. H. & Soltanian-Zadeh, H. Automatic recognition of five types of white blood cells in peripheral blood. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 35, 333–343 (2011).
Google Scholar
Li, C. & Liu, Y. Improved generalization of white blood cell classification by learnable illumination intensity invariant layer. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 31, 176–180 (2024).
Google Scholar
Tsutsui, S., Su, Z. & Wen, B. Benchmarking white blood cell classification under domain shift. In Proc. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2023) (eds Kotropoulos, C. & Narayanan, S.) 1–5 (IEEE, 2023).
Deltadahl, S. et al. CambridgeCIA/CytoDiffusion. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14825813 (2025).
Tavakoli, S., Ghaffari, A., Kouzehkanan, Z. M. & Hosseini, R. New segmentation and feature extraction algorithm for classification of white blood cells in peripheral smear images. Sci. Rep. 11, 19428 (2021).
Google Scholar
Chen, H. et al. Accurate classification of white blood cells by coupling pre-trained ResNet and DenseNet with SCAM mechanism. BMC Bioinform. 23, 282 (2022).
Google Scholar
Jiang, L., Tang, C. & Zhou, H. White blood cell classification via a discriminative region detection assisted feature aggregation network. Biomed. Opt. Express 13, 5246–5260 (2022).
Google Scholar
Rivas-Posada, E. & Chacon-Murguia, M. I. Automatic base-model selection for white blood cell image classification using meta-learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 163, 107200 (2023).
Google Scholar
Ucar, F. Deep learning approach to cell classification in human peripheral blood. In Proc. 5th International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering (UBMK 2020) (ed. Adali, E.) 383–387 (IEEE, 2020).
Rastogi, P., Khanna, K. & Singh, V. LeuFeaTx: deep learning-based feature extractor for the diagnosis of acute leukemia from microscopic images of peripheral blood smear. Comput. Biol. Med. 142, 105236 (2022).
Tummala, S. & Suresh, A. K. Few-shot learning using explainable Siamese twin network for the automated classification of blood cells. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 61, 1549–1563 (2023).
Google Scholar
Chen, M., Mei, S., Fan, J. & Wang, M. An overview of diffusion models: applications, guided generation, statistical rates and optimization. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.07771 (2024).
Ho, J., Jain, A. & Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 6840–6851 (2020).
Song, Y. et al. Score-based generative modeling through stochastic differential equations. In Proc. International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2021) (ICLR, 2021).
Song, Y. & Ermon, S. Improved techniques for training score-based generative models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 12438–12448 (2020).
Sohl-Dickstein, J., Weiss, E., Maheswaranathan, N. & Ganguli, S. Deep unsupervised learning using nonequilibrium thermodynamics. In Proc. International Conference on Machine Learning (eds Bach, F. & Blei, D.) 2256–2265 (PMLR, 2015).
Saharia, C. et al. Photorealistic text-to-image diffusion models with deep language understanding. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 36479–36494 (2022).
Saharia, C. et al. Palette: image-to-image diffusion models. In Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 Conference Proceedings (ed. Mitra, N. J.) 1–10 (ACM, 2022).
Lugmayr, A. et al. RePaint: inpainting using denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (eds Dana, K. et al.) 11461–11471 (IEEE, 2022).
Saharia, C. et al. Image super-resolution via iterative refinement. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 45, 4713–4726 (2022).
van den Oord, A., Vinyals, O. & Kavukcuoglu, K. Neural discrete representation learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30 (2017).
Kingma, D. P. & Welling, M. Auto-encoding variational Bayes. In Proc. 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2014) (ICLR, 2014).
Hang, T. et al. Efficient diffusion training via Min-SNR weighting strategy. In Proc. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision 7441–7451 (IEEE, 2023).
Zhang, H., Cissé, M., Dauphin, Y. N. & Lopez-Paz, D. Mixup: beyond empirical risk minimization. In Proc. International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2018) (ICLR, 2018).
Cubuk, E. D., Zoph, B., Shlens, J. & Le, Q. V. RandAugment: practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space. In Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (eds Dekel, T. & Hassner, T.) 702–703 (IEEE, 2020).
Tan, M. & Le, Q. EfficientNetV2: smaller models and faster training. In Proc. International Conference on Machine Learning (eds Meila, M. & Zhang, T.) 10096–10106 (PMLR, 2021).
Dosovitskiy, A. et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. In Proc. International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2021).
Matek, C., Schwarz, S., Spiekermann, K. & Marr, C. Human-level recognition of blast cells in acute myeloid leukaemia with convolutional neural networks. Nat. Mach. Intell. 1, 538–544 (2019).
Google Scholar
Font, P. et al. Inter-observer variance with the diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) following the 2008 WHO classification. Ann. Hematol. 92, 19–24 (2013).
Google Scholar
Font, P. et al. Interobserver variance in myelodysplastic syndromes with less than 5% bone marrow blasts: unilineage vs. multilineage dysplasia and reproducibility of the threshold of 2% blasts. Ann. Hematol. 94, 565–573 (2015).
Google Scholar
Ho, J. & Salimans, T. Classifier-free diffusion guidance. In NeurIPS 2021 Workshop on Deep Generative Models and Downstream Applications https://openreview.net/pdf?id=qw8AKxfYbI (NeurIPS, 2022).
Don’t miss more hot News like this! Click here to discover the latest in AI news!
2025-11-19 00:00:00