Google quietly launches AI Edge Gallery, letting Android phones run AI without the cloud

Join daily and weekly newsletters to obtain the latest updates and exclusive content to cover the leading artificial intelligence in the industry. Learn more
Google quietly released the experimental Android application that enables users to run advanced artificial intelligence models directly on their smartphones without the need for an internet connection, indicating a great step in pushing the company towards conservative computing and spreading artificial intelligence that focuses on privacy.
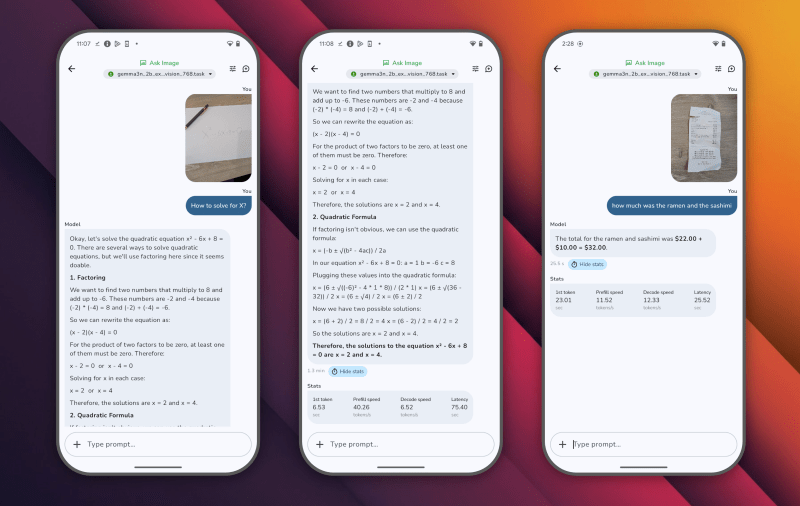
The application, called AI Edge Gallery, allows users to download and implement artificial intelligence models from the fully famous FACE Huging platform on their devices, enable tasks such as images analysis, text generation, coding assistance, and multiple conversations while maintaining all local data processing.
The app, which was released under an open source APACHHE 2.0 license and available through GitHub instead of official application stores, is the latest effort from Google to give the democratic character to access advanced artificial intelligence capabilities while tackling increasing privacy concerns about artificial intelligence services based on the group of the core.
“Google Ai Edge is a trial app that places the power of advanced artificial intelligence models directly in your hands, and it works entirely on your Android devices,” explains Google in the application user guide. “Dive into a world of creative and practical artificial intelligence, all of which work locally, without the need for an internet connection once the form is loaded.”
How to offer lightweight artificial intelligence models from Google performance at the cloud level on mobile devices
The application is based on Google’s Litert platform, previously known as Tensorflow Lite, and MediaPIPE Frameworks, which are specifically improved to run artificial intelligence models on resource -resting mobile devices. The system supports models from multiple machine learning frameworks, including Jax, Keras, Pytorch and Tensorflow.
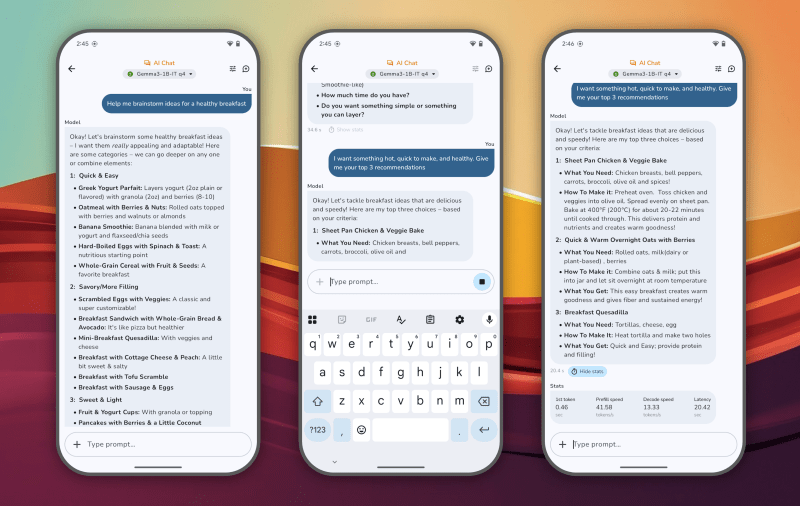
At the heart of the show, there is the Google’s Gemma 3, a 529MB language model that can process up to 2,585 symbols per second while prior concluded on portable graphics processing units. This performance enables sub -response times to tasks such as text generation and images analysis, which makes the experience similar to alternatives based on the group of caspoons.
The application includes three basic capabilities: Amnesty International Chat for multiple conversations, a picture of visual questions, and a laboratory for single tasks such as summarizing the text, generating the code, and rewriting the content. Users can switch between different models to compare performance and capabilities, with actual time standards that show standards such as time specified for time and decomposition.
“InT4 reduces the volume of the model to 4X on 4X via BF16, which reduces the use of memory and cumin.”
Why can AI be processed on the device, a revolution in the privacy of data and the security of the institution
The local processing approach addresses increasing concerns about data privacy in artificial intelligence applications, especially in industries that deal with sensitive information. By maintaining data on the device, institutions can maintain compliance with privacy systems while taking advantage of artificial intelligence capabilities.
This transformation represents a basic re -imagination of the privacy of artificial intelligence. Instead of dealing with privacy as a restriction that reduces the capabilities of artificial intelligence, processing the device turns privacy into a competitive advantage. Organizations no longer need to choose between strong artificial intelligence and data protection – they can have both. The elimination of network dependency also means that intermittent connection, which is traditionally one of the main restrictions of artificial intelligence applications, becomes unrelated to basic functions.
This approach is of special value for sectors such as health care and financing, as data sensitivity requirements often reduce the adoption of Cloud AI. Field applications such as diagnosis of equipment and working scenarios benefit from a distance from the absences related to the Internet.
However, the shift to the device processing provides new safety considerations that institutions must address. Although the data itself becomes safer by never leaving the device, the focus turns into the protection of the devices themselves and artificial intelligence models it contains. This creates new attack tankers and requires different safety strategies from the traditional cloud -based publishing operations. Institutions must now consider managing the fleet of devices, verifying typical integrity, and protecting against hostile attacks that can display local artificial intelligence systems.
The Google platform strategy targets the goal of Apple and Qualcomm from artificial intelligence
Google’s step comes in intensive competition in the mobile space. The Apple nervous engine, which is included via iPhone, iPads and MacS, is already running the actual time processing and arithmetic photography on the device. The AI Qualcomm engine, created in Snapdragon chips, drives sound recognition and smart aids on Android smartphones, while Samsung uses neurotransmitters included in galaxy devices.
However, the Google approach is greatly different from competitors by focusing on the infrastructure of the statute instead of royal features. Instead of competing directly for the specific AI capabilities, Google places itself as a basic layer that enables all mobile AI applications. The frequency of this strategy is that a successful statute plays from the history of technology, as the infrastructure control is more valuable than controlling individual applications.
The timing of this platform strategy is particularly shrewd. When mobile artificial intelligence capabilities become a commodity, the real value turns into those who can provide tools, frameworks and distribution mechanisms that developers need. By using open -minded sources and making it widely available, Google guarantees wide dependence while maintaining control of the basic infrastructure that operates the entire ecosystem.
What the early test reveals about the current challenges and restrictions of Mobile AI
The application is currently facing many restrictions that confirm its experimental nature. Performance varies greatly based on device devices, with advanced devices such as Pixel 8 Pro that deal with the smoothly larger styles while medium -level devices may face a higher transition time.
The test revealed accuracy problems with some tasks. The app sometimes provided incorrect responses to specific questions, such as incorrectly identifying the crew of the fictional spacecraft or wrong photo books. Google acknowledges these restrictions, as artificial intelligence stated itself during the test that it “is still under development and is still learning.”
The installation remains exhausted, which requires users to enable the developer position on Android devices and manually install the application via APK files. Users should also create embraced facial accounts to download models, add friction to the movement.
The restrictions of the devices highlight the basic challenge facing artificial intelligence: the tension between the development of the model and the restrictions of the devices. Unlike cloud environments where almost almost border resources can be limited, portable devices should balance the performance of artificial intelligence against battery life, thermal management and memory restrictions. This forces the developers to become experts in improving efficiency rather than taking advantage of the raw mathematical force.
The quiet revolution that can reshape the future of artificial intelligence lies in your pocket
Google’s Edge Ai is more than just another trial application. The company launched the opening fire while it could become the largest transformation in artificial intelligence since the emergence of cloud computing two decades ago. While technology giants have spent years building huge data centers to operate artificial intelligence services, Google is now betting that the future belongs to billions of smartphones that people already carry.
This step goes beyond technical innovation. Google wants to change the extent of users’ association with their personal data. Privacy violations dominate the main headlines, and organizers all over the world do not exceed data collection practices. Google’s transformation towards local processing of companies and consumers provides a clear alternative to the monitoring business model that has worked on the Internet for years.
Google timing this strategy carefully. Companies are struggled with artificial intelligence governance rules while consumers grow increasingly on data privacy. Google puts itself as a basis for the distributed artificial intelligence system instead of competing directly with the tightly integrated Apple or Qualcomm foil. The company builds the infrastructure layer that can manage the next wave of artificial intelligence applications across all devices.
Current problems related to the application – difficult installation, accidental wrong answers, and changing performance across devices – where Google improves technology. The biggest question is whether Google can manage this transition while maintaining its dominant position in the artificial intelligence market.
Edge AI reveals Google that the central artificial intelligence model that helped its construction may not last. Google opens its tools and makes Amnesty International on the device widely available because it believes that the infrastructure control of artificial intelligence tomorrow is more than possessing databases today. If the strategy succeeds, each smartphone becomes part of the Google AI network. This possibility makes the launch of this quiet application much more important than the experimental poster.
Don’t miss more hot News like this! Click here to discover the latest in Technology news!
2025-06-02 20:46:00





