Introducing Gemma 3n: The developer guide

Gemma’s first mod launched early last year and has since grown into a thriving Gemmaverse with over 160 million collective downloads. This ecosystem includes our family of more than a dozen specialized models for everything from protection to medical applications and, most inspiringly, countless innovations from the community. From innovators like Roboflow building enterprise computer vision to the Tokyo Science Institute creating highly capable Japanese Gemma variants, your work has shown us the way forward.
Building on this amazing momentum, we are excited to announce the full release of Gemma 3n. Although last month’s preview provided a glimpse, today reveals the full power of this mobile-first architecture. Gemma 3n is built for the developer community that helped shape Gemma. It’s powered by your favorite tools including Hugging Face Transformers, llama.cpp, Google AI Edge, Ollama, MLX, and many others, allowing you to easily configure and deploy your device-specific apps. This post is a developer deep dive: we’ll explore some of the innovations behind Gemma 3n, share new benchmarking results, and show you how to start building today.
What’s new in Gemma 3n?
Gemma 3n represents a major advance in on-device AI, bringing powerful multimedia capabilities to the edge with performance only seen in frontier cloud-based models of the past year.
Achieving this leap in performance on device requires rethinking the model from the ground up. The foundation is Gemma 3n’s unique mobile architecture, and it all starts with MatFormer.
MatFormer: One form, multiple sizes
At the heart of Gemma 3n is… MatFormer (Matryoshka converter) Build,A new nested transformer designed for flexible inference. Think of it like Matryoshka dolls: the larger model contains smaller, fully functioning versions of itself. This approach expands the concept of learning a Matryoshka representation from mere embedding to all transformer components.
While MatFormer is training the effective parameter 4B (E4B) model, the effective parameter 2B (E2B) submodel within it is optimized at the same time, as shown in the figure above. This provides developers with powerful capabilities and use cases today:
1: Pre-extracted models: You can download and use either the main E4B model directly for the highest potential, or the standalone E2B sub-model that we have already extracted for you, providing up to 2x faster inference.
2: Custom Sizes with Mix-n-Match: For more detailed control tailored to specific hardware limitations, you can create a set of custom-sized models between E2B and E4B using a method we call Mix-n-Match. This technology allows you to precisely partition the parameters of the E4B model, mainly by adjusting the hidden dimension of the feed-forward mesh for each layer (from 8192 to 16384) and selectively skipping some layers. We have released MatFormer Lab, a tool that shows how to recover these ideal models, which are identified by evaluating different settings on benchmarks such as MMLU.
MMLU scores for pre-trained Gemma 3n checkpoints with different model sizes (using Mix-n-Match)
Looking to the future, MatFormer architecture also paves the way Flexible implementation. Although not part of the applications launched today, this capability allows a single deployed E4B model to dynamically switch between E4B and E2B inference paths on the fly, enabling optimization of performance and memory usage in real-time based on the current task and machine load.
Per-Layer Embeddings (PLE): Unlock more memory efficiency
Includes Gemma 3n models Per-layer embeddings (PLE). This innovation is designed for on-device deployment because it significantly improves model quality without increasing the high-speed memory space required on your device accelerator (GPU/TPU).
While the Gemma 3n E2B and E4B models have a total number of parameters of 5B and 8B respectively, PLE allows a large portion of these parameters (the embeddings associated with each layer) to be loaded and computed efficiently on the CPU. This means that only the core switch weights (about 2B for E2B and 4B for E4B) need to sit in the typically more restricted accelerator memory (VRAM).
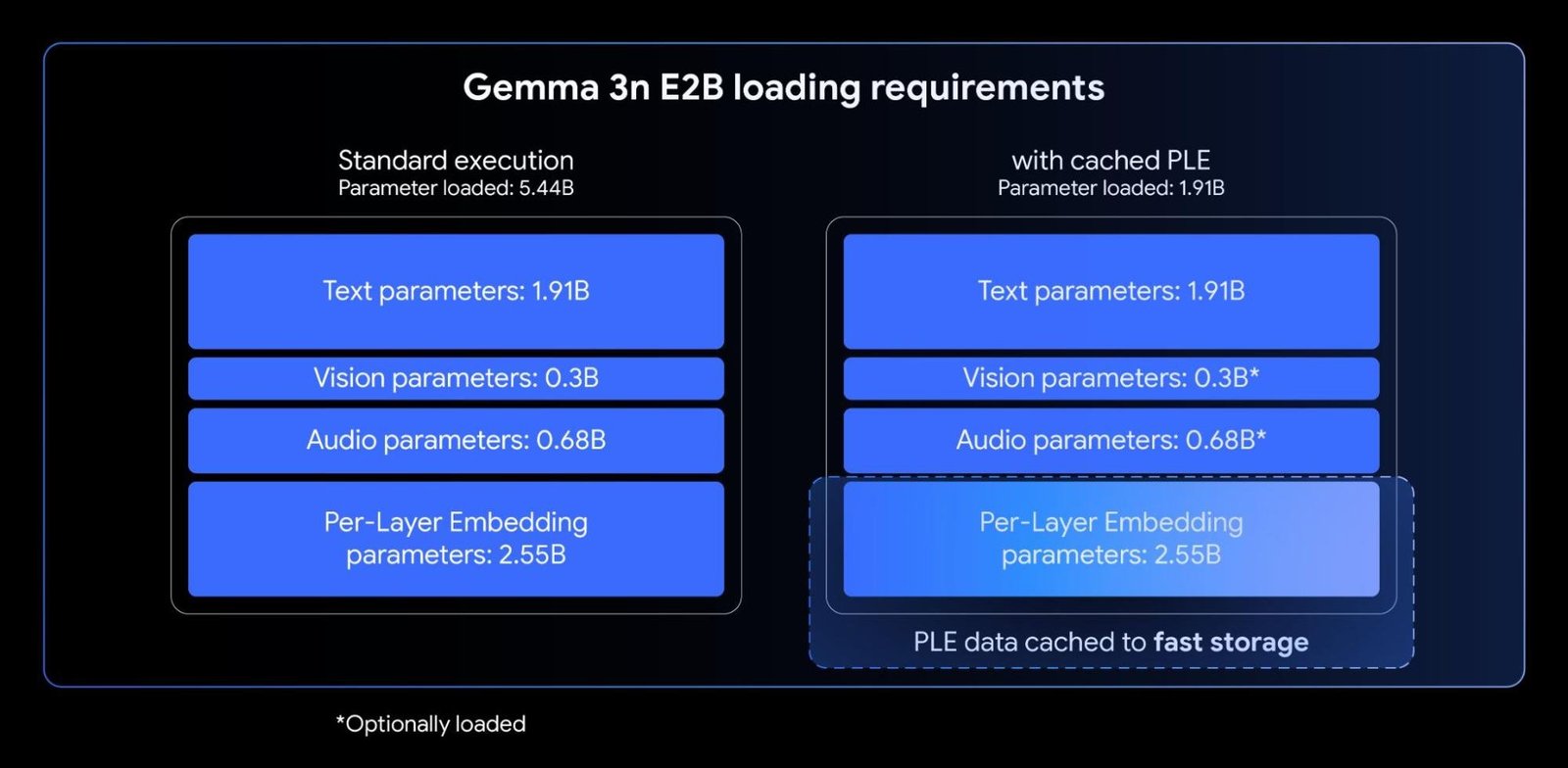
Using per-layer embeddings, you can use Gemma 3n E2B with only ~2B parameters loaded into your accelerator.
KV cache sharing: faster long context processing
Processing long inputs, such as sequences derived from audio and video streams, is essential for many advanced on-device multimedia applications. Gemma 3n offers KV Cache Sharing, a feature designed to dramatically speed up the time to first token for stream response applications.
KV cache sharing improves how the model handles the initial input processing phase (often called the “pre-packing” phase). The middle layer’s keys and values of local and global interest are shared directly with all upper layers, providing a significant 2x improvement in prepackaging performance compared to Gemma 3 4B. This means that the model can absorb and understand long prompt sequences much faster than before.
Audio understanding: Speech-to-text input and translation
Gemma 3n uses an advanced voice encoder based on the Universal Speech Model (USM). The encoder generates a token for every 160 milliseconds of audio (about 6 tokens per second), which is then integrated as input into the language model, providing an accurate representation of the audio context.
This integrated audio capability unlocks key features for on-device development, including:
- Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR): Enable high-quality speech-to-text conversion directly on the device.
- Automatic speech translation (AST): Translating spoken language into text in another language.
We observed particularly strong AST results for translation between English, Spanish, French, Italian, and Portuguese, offering great potential for developers targeting applications in these languages. For tasks such as speech translation, leveraging the train of thought can greatly enhance results. Here is an example:
user
Transcribe the following speech segment in Spanish, then translate it into English:
model Plain text
At launch time, the Gemma 3n encoder is used to process audio clips up to 30 seconds long. However, this is not the primary limitation. Basic Audio Encoder is a streaming encoder, capable of processing arbitrarily long audio recordings with additional long audio training. Subsequent implementations will open low-latency and long streaming applications.
MobileNet-V5: A new advanced vision encoder
Along with its integrated audio capabilities, Gemma 3n features a new high-efficiency vision encoder, MobileNet-V5-300Mproviding cutting-edge performance for multimedia tasks on high-end devices.
Designed for flexibility and capacity on limited devices, MobileNet-V5 offers developers:
- Multiple input resolutions: Natively supports 256 x 256, 512 x 512, and 768 x 768 pixel resolutions, allowing you to balance performance and detail for your specific applications.
- Extensive visual understanding: Jointly trained on large-scale multi-modal datasets, it excels on a wide range of image and video understanding tasks.
- High productivity: Processes up to 60 frames per second on Google Pixel, enabling real-time video analysis on the device and interactive experiences.
This level of performance is achieved through multiple architectural innovations, including:
- Advanced foundation for MobileNet-V4 clusters (including global inverted bottlenecks and Mobile MQA).
- A significantly improved architecture, featuring a hybrid deep hierarchical model that is 10 times larger than the largest MobileNet-V4 variant.
- New multi-scale VLM Fusion VLM converter that improves symbol quality for better accuracy and efficiency.
Leveraging new architectures and advanced distillation techniques, MobileNet-V5-300M significantly outperforms the SoViT baseline on Gemma 3 (which was trained using SigLip, without distillation). On the Google Pixel Edge TPU, it is Provides a 13x speedup with quantization (6.5x without), requires 46% fewer parameters, and has a 4x smaller memory footprintAll while providing much higher accuracy on visual language tasks
We’re excited to share more about the work behind this model. Stay tuned for our next technical report on MobileNet-V5, which will delve into model architecture, data scaling strategies, and advanced distillation techniques.
Making Gemma 3n accessible from day one has been a priority. We’re proud to partner with many amazing open source developers to ensure broad support across popular tools and platforms, including contributions from the teams behind AMD, Axolotl, Docker, Hugging Face, llama.cpp, LMStudio, MLX, NVIDIA, Ollama, RedHat, SGLang, Unsloth, and vLLM.
But this ecosystem is just the beginning. The real power of this technology is what you build with it. That’s why we’re launching the Gemma 3n Impact Challenge. Your mission: Use Gemma 3n’s unique on-device, offline, and multimedia capabilities to build a product for a better world. With $150,000 in prizes, we’re looking for a compelling video story and an “amazing” demo that shows real-world impact. Join the challenge and help build a better future.
Get started with Gemma 3n today
Are you ready to explore the potential of Gemma 3n today? Here’s how:
- Experience directly: Use Google AI Studio to experience Gemma 3n with just a few clicks. Gemma models can also be published directly to Cloud Run from AI Studio.
- Learning and integration: Dive into our comprehensive documentation to quickly integrate Gemma into your projects or get started with our precise inference and tuning guides.
Don’t miss more hot News like this! Click here to discover the latest in AI news!
2025-10-25 17:54:00




