Meet the researchers testing the “Armageddon” approach to asteroid defense
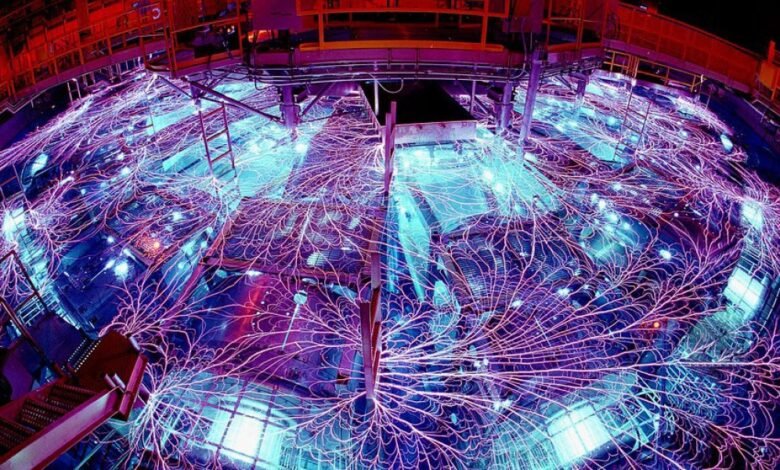
Surrounded by Klaxons and flashing lights, it is a frightening scene. “It is the size of the building – the three floors are prolonged,” says Moore. Each launch of the z machine holds more than 1,000 thunderbolt screws, and each shot lasts a few million seconds: “You cannot even close this quickly.” The Z for its active molecules is called, but Z can easily stand for “Zeus”.
Randy Montoya/National Sandia Laboratory
The original purpose of the Z, whose first shape was constructed half a century ago was nuclear integration research. But over time, it was tampered with, promoted and used for all types of science. “The Z machine was used to compress the material with the same density [you’d find at] Planetary centers. Moore says, for example, can easily be used as a pre-nature device, and the energies of the pre-nature device can be used, and can be used easily to generate X-rays-in this case, for example, pre-nature machine energies can be used, and natural machine energies can be used better to generate X-rays-in this case, by electrifying and finishing argon gas cloud.
“The idea of studying an asteroid deviation is completely different for us,” said Moore. “The device” shoots only once a day, “he says, so all experiments are planned more than a year ago. In other words, researchers had to be near one experience that would work, or would be long waiting to try again – if they are allowed to try a second attempt.
For some time, they could not know how to hang their accurate tools. But in the end, they found a solution: it will incredibly perform two thin pieces of aluminum chips to holding their goals in its place in the Z Machine room. When the X -ray explosion and targets strike them, cutting chips will be evacuated immediately, leaving goals for a short period hanging in the room and allowing them to retreat as if they were in space. Moore says about the chips. This technique was called “X -ray scissors”.
In July 2023, after a great planning, the team was ready. Inside the space room Z Machine there were two nail-size goals-part of quartz and some molten silica, both of which are frequently present on real asteroids. Near, a pocket moved from argon gas. Satisfied that the giant Jazmo was ready, everyone left and went to stand in the control room. For a moment, she was calm.
comment.
fire.
It ended before their ears could record a metal. The storm of electricity shocked the argon gas cloud, causing its collapse; As she did, she turned into a plasma and shouted X -rays from him, racing towards both goals in the room. The chip disappeared, the surfaces of both goals erupted out as a transnational tramps of debris, and the targets went back, away from X -rays, 160 miles per hour.
Moore was not there. “I was in Spain when the experiment was run, because I was celebrating the anniversary of my wife, and there was no way to miss it,” he says. But immediately after the launch of the Z, one of his colleagues sent him a very brief text: he succeeded.
“We immediately knew that it was a great success,” said Moore. The effects were immediately clear. The experimental preparation was complicated, but they were trying to achieve something very essential: a demonstration in the real world that the nuclear explosion could make an object in the movement of space.
“We are really looking into this from the point of view.” This technique can save lives. “
Patrick King, a physicist in the Applied Physics Laboratory at Johns Hopkins University. Previously, pushing the back objects using X -rays was very difficult in the laboratory. “They managed to obtain a direct measurement to transport momentum,” he says, describing X -ray scissors as an “elegant” technique.
Don’t miss more hot News like this! AI/" target="_blank" rel="noopener">Click here to discover the latest in AI news!
2025-04-14 09:00:00