Meta AI Releases Omnilingual ASR: A Suite of Open-Source Multilingual Speech Recognition Models for 1600+ Languages
How do you create a single speech recognition system that can understand thousands of languages, including many that did not have ASR (automatic speech recognition)?) models before? Meta AI has released Omnilingual ASR, an open source speech recognition suite that spans over 1,600 languages and can be expanded to unseen languages with only a few speech text examples, without retraining the model.
Data coverage and language
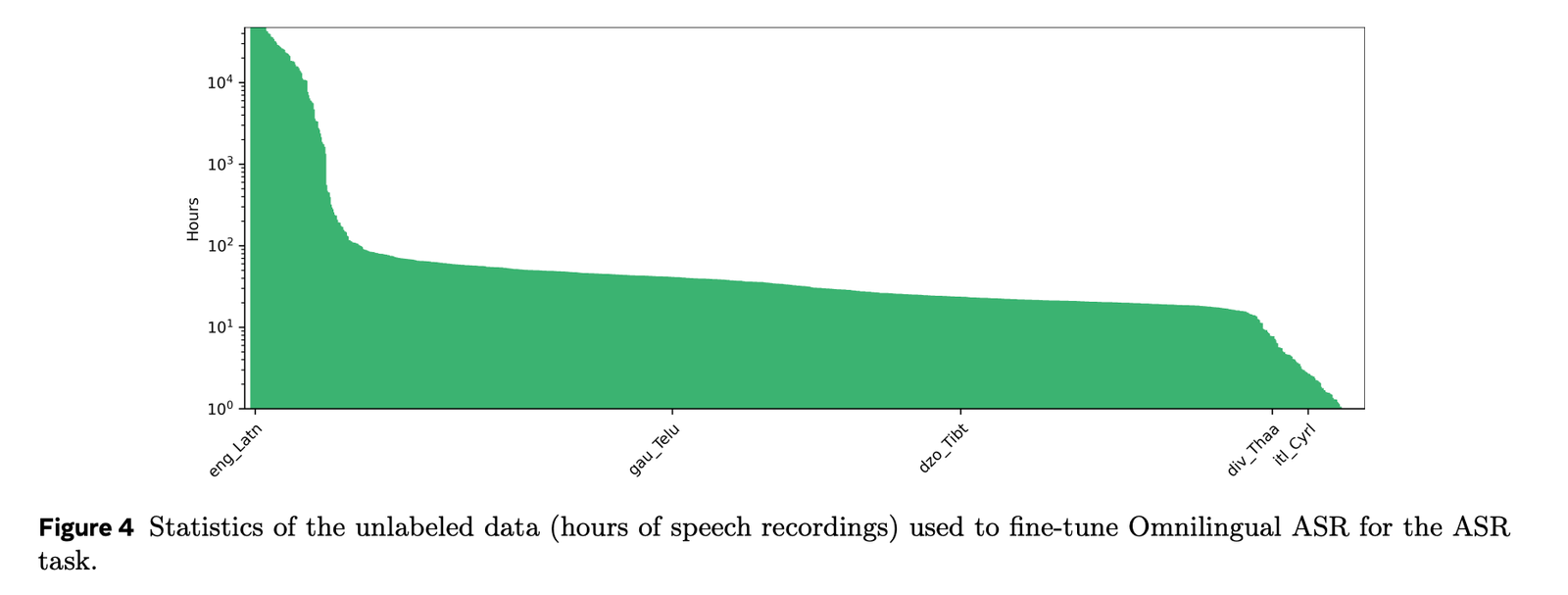
The supervised training data comes from a shared collection called AllASR. AllASR contains 120,710 hours of labeled speech paired with text across 1,690 languages. This collection integrates several sources, including open source datasets, internal and licensed collections, data created by partners, and a delegated collection called ASR group is multilingual.
The multilingual ASR collection contributes 3,350 hours of speech for 348 languages, with data collected through fieldwork with local organizations and speakers in regions such as Africa and South Asia. The stimuli are open-ended, so speakers produce natural monologues in their own language rather than reading fixed sentences, giving more realistic phonological and lexical variation.

For self-supervised pre-training, wav2vec 2.0 encoders are trained on a large corpus of unlabeled speech. The pre-training dataset contains 3.84 million hours of speaking with language selection across 1,239 languages, plus another 460,000 hours without language selection. Thus the total unlabeled audio used for pre-training is approximately 4.3 million hours. This is still far less than the 12 million hours used in USM, which makes the reported results even more interesting from a data efficiency perspective.

Model family
Multilingual ASR features three main model families that all share the same wav2vec 2.0 speech encoder backbone:
- SSL encryption (OmniASR W2V)
Self-supervised wav2vec 2.0 encoders with the following parameter numbers
•omniASR_W2V_300MWith 317,390,592 parameters
•omniASR_W2V_1BWith 965,514,752 parameters
•omniASR_W2V_3BWith 3,064,124,672 parameters
•omniASR_W2V_7BWith 6,488,487,168 parameters. These models are trained using the standard wav2vec 2.0 variational target. After training, the measuring device is discarded and the encoder is used as the backbone for the speech representation. - CTC (Associative Temporal Classification) ASR models
CTC models add a simple linear layer on top of the encoder and train end-to-end with character-level CTC loss. Released CTC models range from 325,494,996 parameters to 6,504,786,132 parameters and reach real-time factors of up to 0.001 for the 300M model on the A100 for 30-second audio with batch size 1. - LLM ASR models
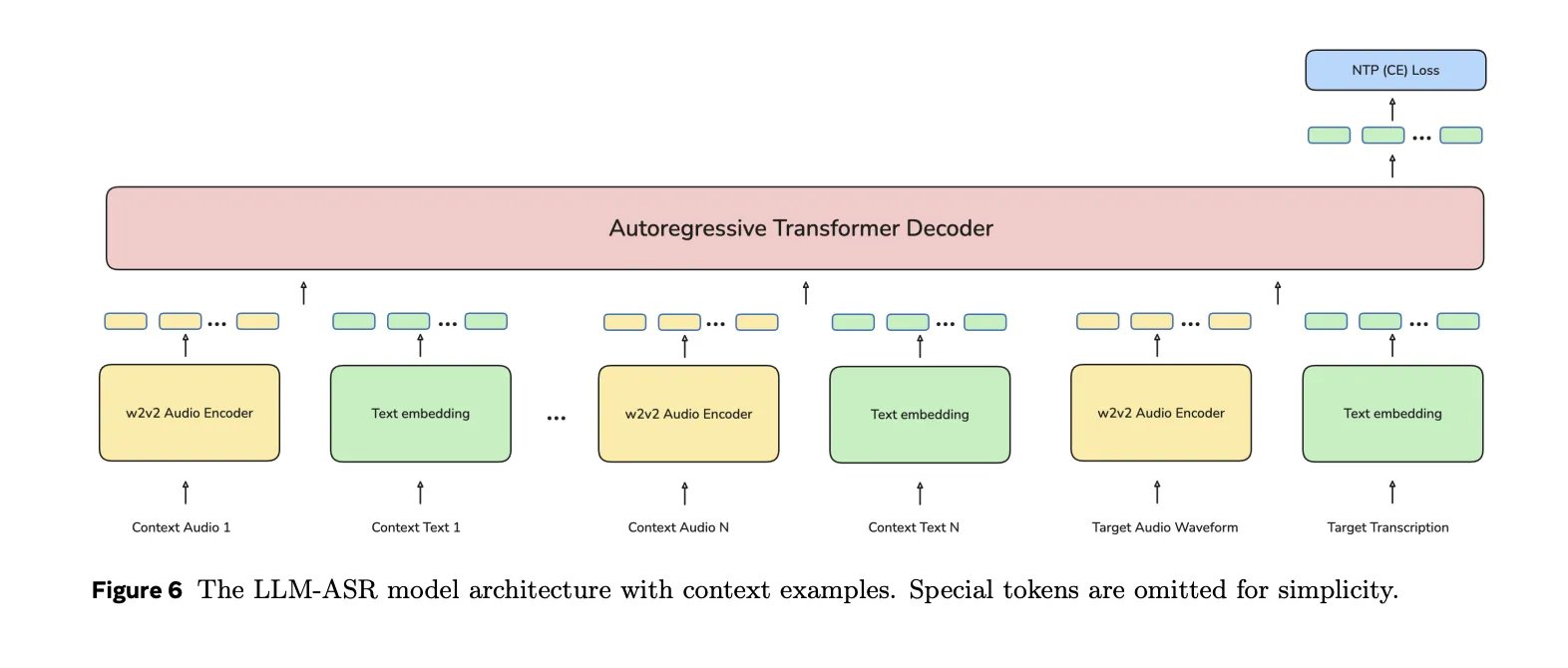
The LLM ASR stacks a transformer decoder on top of the wav2vec 2.0 encoder. A decoder is a language model such as a Transformer that operates on character level tokens as well as tokens such asgs(x), gt(where), gt(y), gt( ) gsIt is a speech encoding programgtIt is the text embedding matrix. The LLM ASR family ranges from approximately 1.63 billion parametersomniASR_LLM_300MTo 7,801,041,536 parameters foromniASR_LLM_7B. separateomniASR_LLM_7B_ZSA checkpoint containing 7,810,900,608 parameters is used to zero the ASR shot.
All LLM ASR modules support optional language adaptation. Languages are represented as {language_code}_{script} like eng_Latn For English in Latin text or cmn_Hans For Mandarin Chinese in Simplified Chinese script. The acquired embedding of the language script identifier is fed into the input of the decoder. In training, the language identifier code is sometimes dropped, so the model can also work without explicit language tags when inferring.
Zero shot ASR with context and sonar examples
Supervised models cover more than 1,600 languages. However, many languages still do not have written ASR statements. To handle these cases, Omnilingual ASR extends the LLM ASR model with zero-shot mode trained using context examples.
During training on the zero-shot variant, the decoder is consumed N + 1 Text-to-speech pairs from the same language. the first N The pairs act as context and the last pair is the target. All pairs are embedded with a speech encoder and text embedding matrix, and then concatenated into a single decoder input sequence. Loss is still the next symbolic prediction on target replication. This teaches the decoder to infer the mapping from speech to text in a given language from a small wave of linguistic examples.
In inference, omniASR_LLM_7B_ZS The model can receive some text examples of speech from any language, including languages not in training, and then transcribe new utterances in that language without updating the weights. This is in the context of learning for ASR.
The system includes an example of a retrieval mechanism based on SONAR, a multilingual multimedia encoder that projects audio and text into a common embedding space. The target phoneme is included once, and then a nearest-neighbor search across a database of speech-text pairs selects the most relevant examples to include in the context window. This SONAR-based selection improves zero-snap performance compared to selecting random examples or simple text similarity.

Quality and standards
the omniASR_LLM_7B The model achieves a character error rate of less than 10 percent for 78 percent of more than 1,600 supported languages.
The research team reports that in multilingual benchmarks such as FLEURS 102, the 7B LLM ASR model outperforms the 7B CTC models and also outperforms the Google USM variants in average character error rate, despite using about 4.3 million unnamed hours instead of 12 million and a simpler pre-training path. This indicates that extending the wav2vec 2.0 encoder and adding an LLM style decoder is an effective path for high-coverage multilingual ASR.
Key takeaways
- Multilingual ASR Provides open source ASR coverage for over 1,600 languages and can be generalized to over 5,400 languages using zero shot at contextual learning.
- The models are built on large-scale wav2vec 2.0 encoders trained on approximately 4.3 million hours of unlabeled audio from 1,239 labeled languages plus additional unlabeled speech.
- The suite includes wav2vec 2.0 encoders, a CTC ASR, an LLM ASR, and a dedicated zero-shot LLM ASR model, with encoder sizes ranging from 300 million to 7B parameters and an LLM ASR of up to about 7.8 billion parameters.
- The 7B LLM ASR model achieves a character error rate of less than 10 percent in 78 percent of more than 1,600 supported languages, which rivals or outperforms previous multilingual systems in low-resource settings.
Multilingual ASR is a major systems-level contribution because it treats multilingual ASR as an extensible framework, not as a fixed language list, combining the 7B wav2vec 2.0 encoder and CTC and LLM ASR decoders, and a launchless LLM ASR model that can adapt to new languages with only a few examples in context, achieving a character error rate of less than 10 percent in 78 percent of over 1,600 supported languages and launching everything under Apache. 2.0 and CC BY 4.0. Overall, this launch solidifies the multilingual ASR system as the most extensible open source speech recognition model currently available.
verify Paper, repo and Technical details. Feel free to check out our website GitHub page for tutorials, codes, and notebooks. Also, feel free to follow us on twitter Don’t forget to join us 100k+ mil SubReddit And subscribe to Our newsletter. I am waiting! Are you on telegram? Now you can join us on Telegram too.

Michel Sutter is a data science specialist and holds a Master’s degree in Data Science from the University of Padova. With a solid foundation in statistical analysis, machine learning, and data engineering, Michelle excels at transforming complex data sets into actionable insights.
🙌 FOLLOW MARKTECHPOST: Add us as a favorite source on Google.
Don’t miss more hot News like this! Click here to discover the latest in AI news!
2025-11-11 09:06:00




