Nanbeige4-3B-Thinking: How a 23T Token Pipeline Pushes 3B Models Past 30B Class Reasoning
Can the 3B model advance 30B class thinking by fixing the training recipe instead of measuring parameters? The Nanbeige LLM Lab at Boss Zhipin has released Nanbeige4-3B, a family of small 3B parameterized language models trained with an unusually strong focus on data quality, curriculum scheduling, distillation, and reinforcement learning.
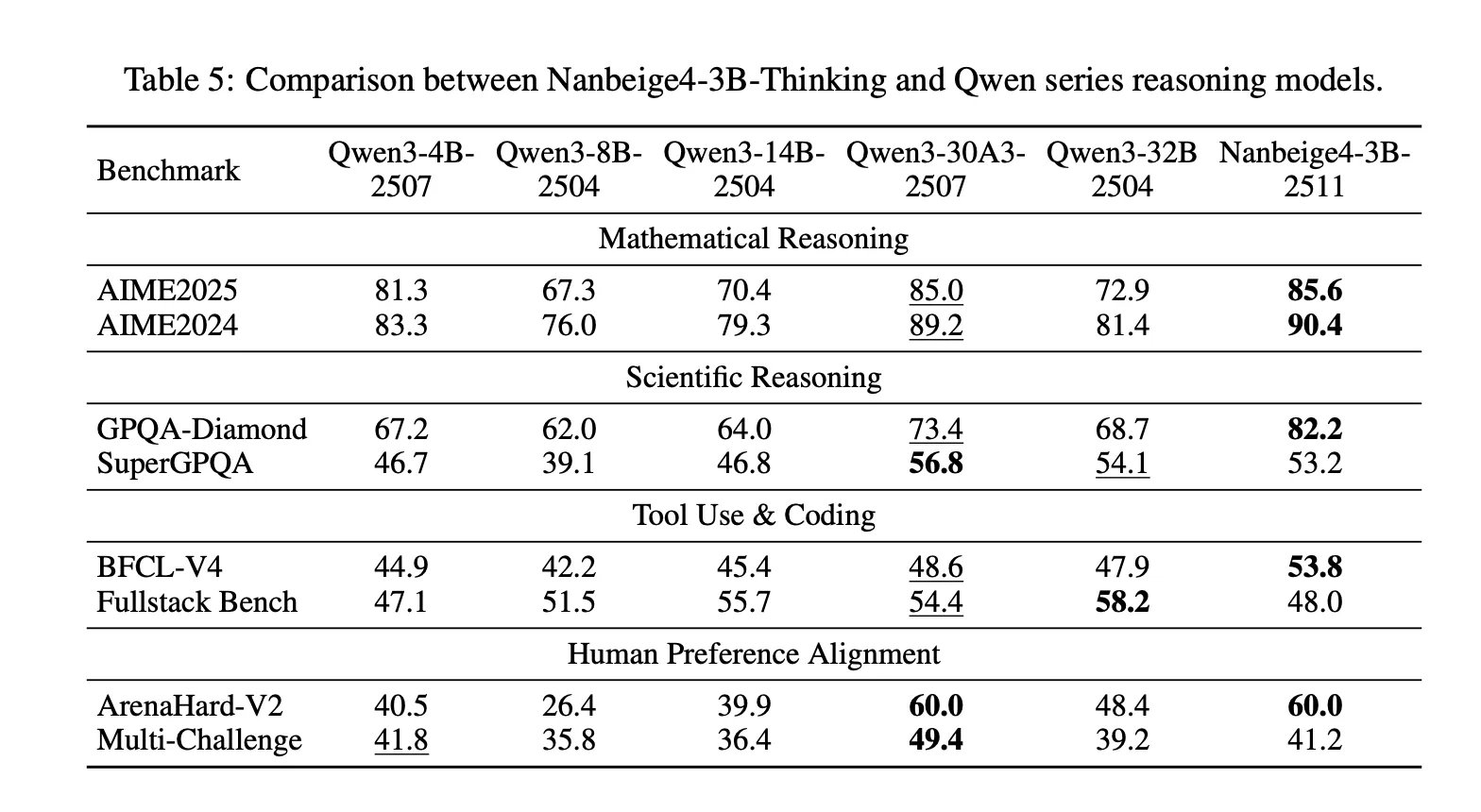
The research team ships two basic checkpoints, Nanbeige4-3B-Base and Nanbeige4-3B-Thinking, and evaluates the heuristics tuning model against Qwen3 checkpoints from 4B to 32B parameters.

Reference results
At AIME 2024, Nanbeige4-3B-2511 reported 90.4, while Qwen3-32B-2504 reported 81.4. On GPQA-Diamond, Nanbeige4-3B-2511 reported 82.2, while Qwen3-14B-2504 reported 64.0 and Qwen3-32B-2504 reported 68.7. These are the two criteria where the “3B outperforms 10x larger” research framework is directly supported.
The research team also shows strong gains in tool utilization in BFCL-V4, with Nanbeige4-3B reporting 53.8 versus 47.9 for Qwen3-32B and 48.6 for Qwen3-30B-A3B. In Arena-Hard V2, the Nanbeige4-3B scored 60.0, matching the highest score listed in the comparison table within the research paper. At the same time, the model is not the best in every category, on Fullstack-Bench it is 48.0, lower than the Qwen3-14B at 55.7 and the Qwen3-32B at 58.2, and on SuperGPQA it is 53.2, slightly lower than the Qwen3-32B at 54.1.

The training recipe, the parts that drive the 3B model
Hybrid data filtering, then large-scale resampling
For pre-training, the research team combines multidimensional labeling with similarity-based scoring. They reduce their labeling space to 20 dimensions and report two main results: Content-related labels are more predictive than format labels, and a fine-grained 0–9 scoring system outperforms binary classification. In order to score based on similarity, they built a retrieval database containing hundreds of billions of entries that supports mixed text retrieval and vector retrieval.
They filter out 12.5T tokens from the high-quality data, then select a higher-quality subset of 6.5T and aggregate them for two or more epochs, resulting in a final training set of 23T tokens. This is the first place where the report deviates from the typical small-scale training, and the pipeline is not limited to “clean data,” but is recorded, retrieved, and reshaped using clear utility assumptions.
FG-WSD, utility data tabulator instead of uniform sampling
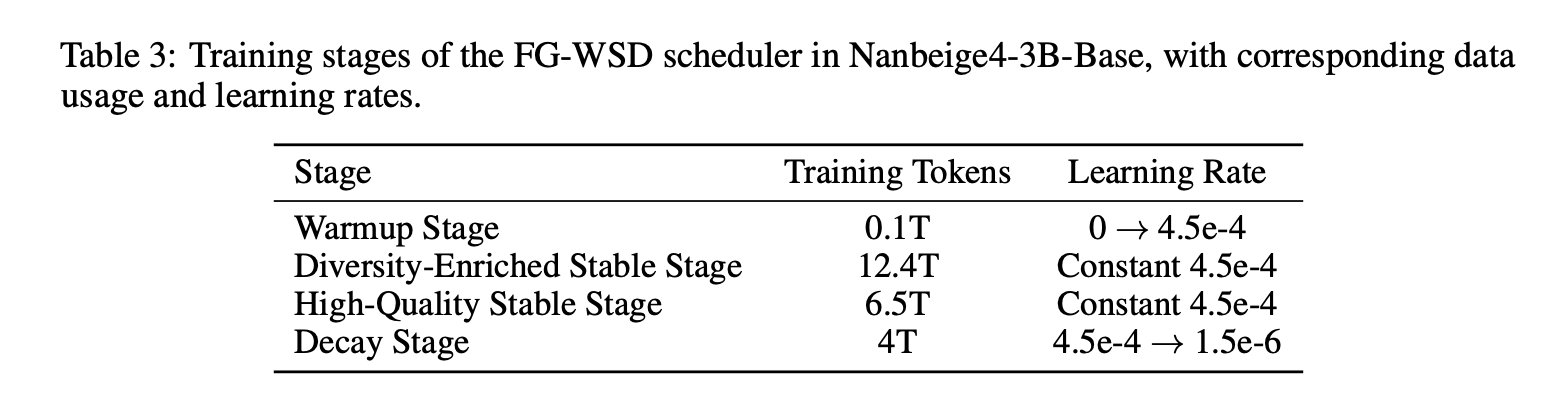
Most similar research projects treat steady-state warm-up decay as a learning rate schedule only. Nanbeige4-3B adds an in-phase stable data approach via FG-WSD, Fine-Grained Warmup-Stable-Decay. Instead of sampling a fixed mixture throughout stable training, they concentrate progressively higher quality data later in training.
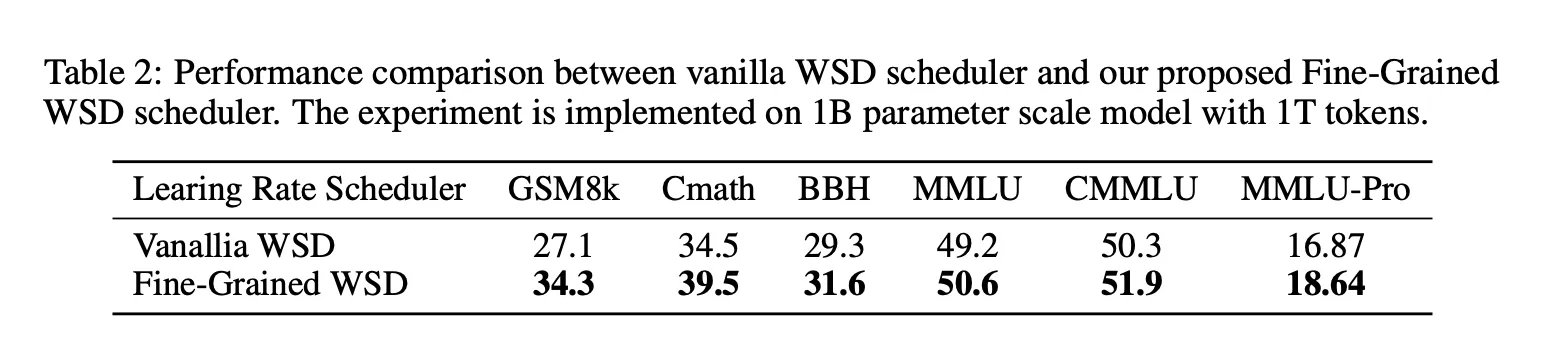

In a 1B ablation trained on 1T codes, the table above shows GSM8K improving from 27.1 under Vanilla WSD to 34.3 under FG-WSD, with gains across CMATH, BBH, MMLU, CMMLU, and MMLU-Pro. In the full Round 3B, the research team splits the training into Warmup, Diversity-Enriched Stable, High-Quality Stable, and Deay, and uses ABF in the decay phase to expand the context length to 64 KB.

Multistage SFT,then fix the supervision effects
Subsequent training begins with cold start SFT, then general SFT. The cold start phase uses approximately 30M QA samples focused on mathematics, science, and code, with a context length of 32K, and a reported mix of approximately 50% mathematical reasoning, 30% scientific reasoning, and 20% code assignments. The research team also claims that scaling cold start SFT instructions from 0.5M to 35M maintains the improvement of AIME 2025 and GPQA-Diamond, with no early saturation in their experiments.
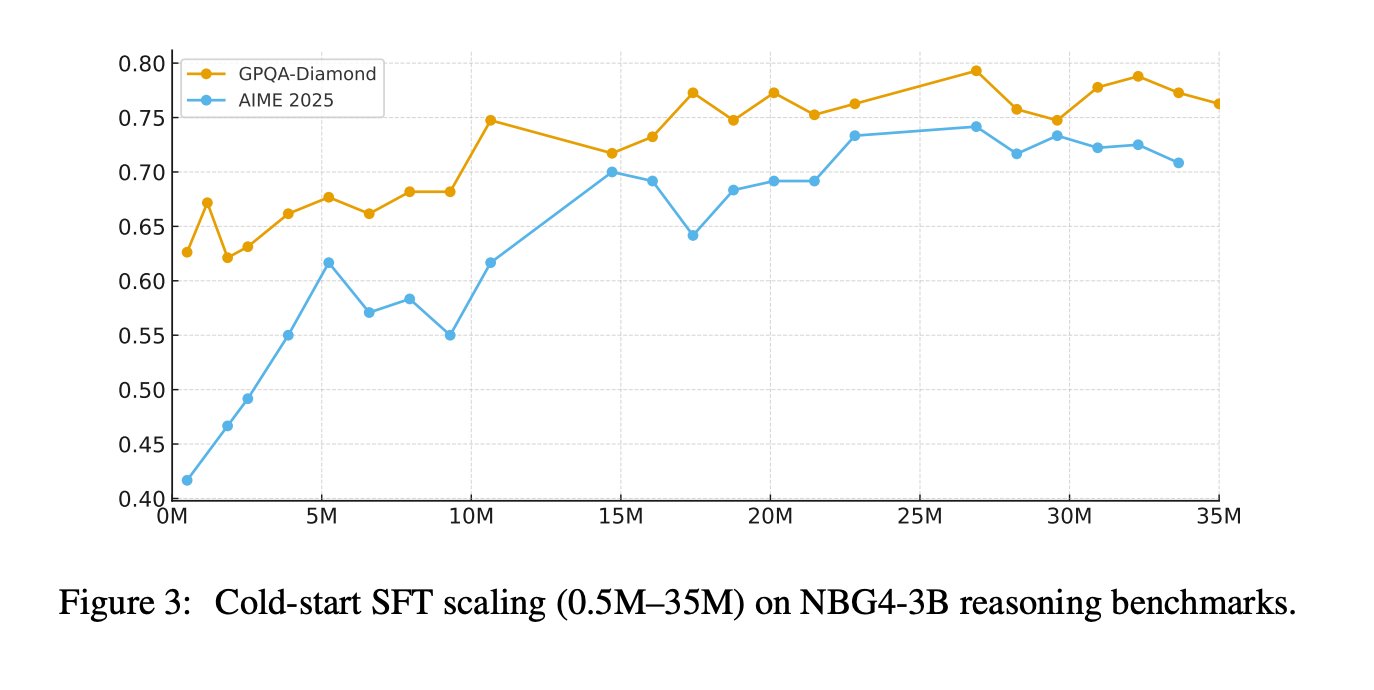

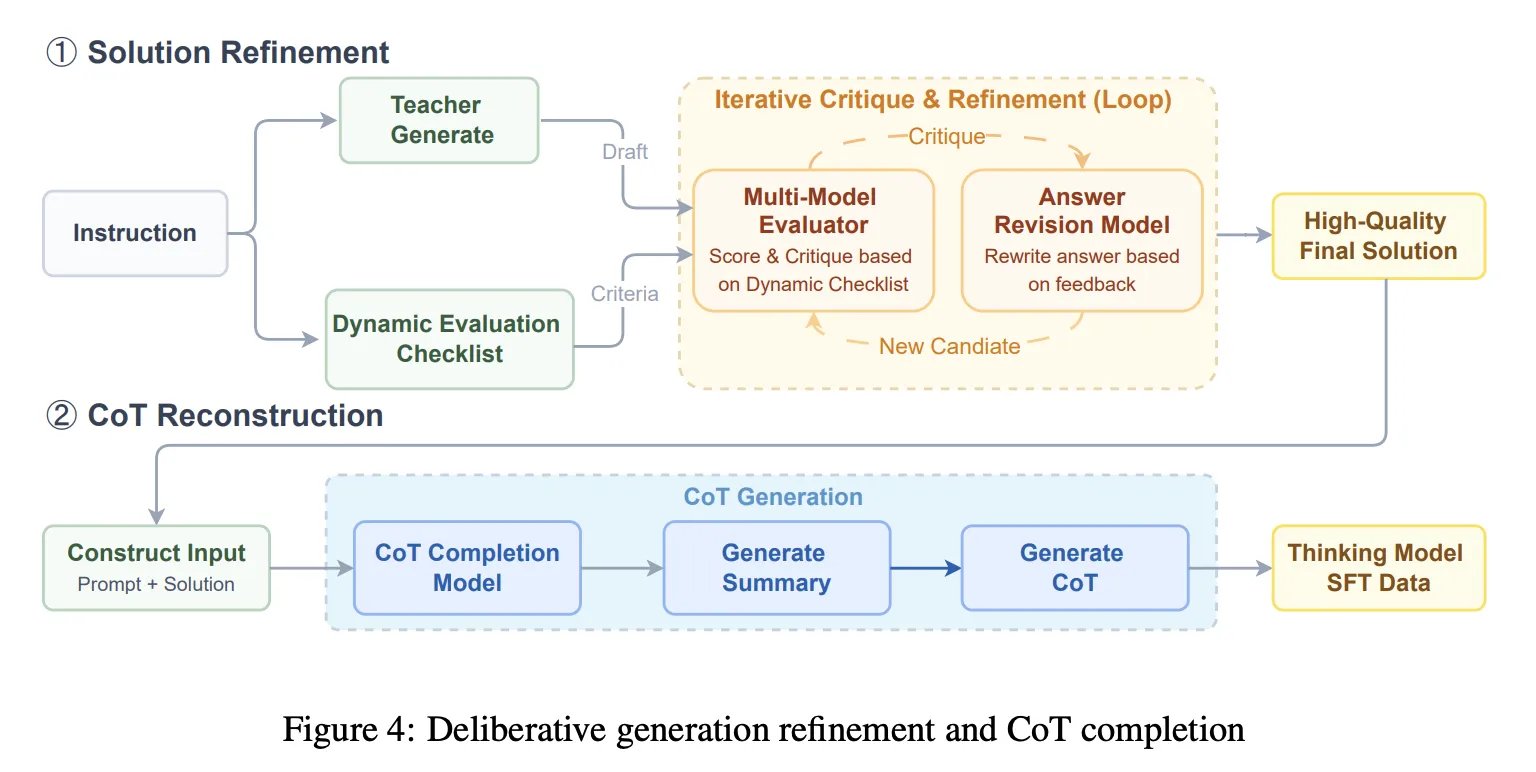
SFT generally turns out to be a combination of 64KB context length including general conversation, writing, agent style tool use, planning, more difficult reasoning targeting vulnerabilities, and programming tasks. This stage provides improvement of the solution as well as reconstruction of the chain of ideas. The system runs iterative generation, critique, and review cycles guided by a dynamic checklist, and then uses a chain completion model to reconstruct a coherent CoT that conforms to the final refined solution. This is intended to avoid training broken heuristics after extensive editing.

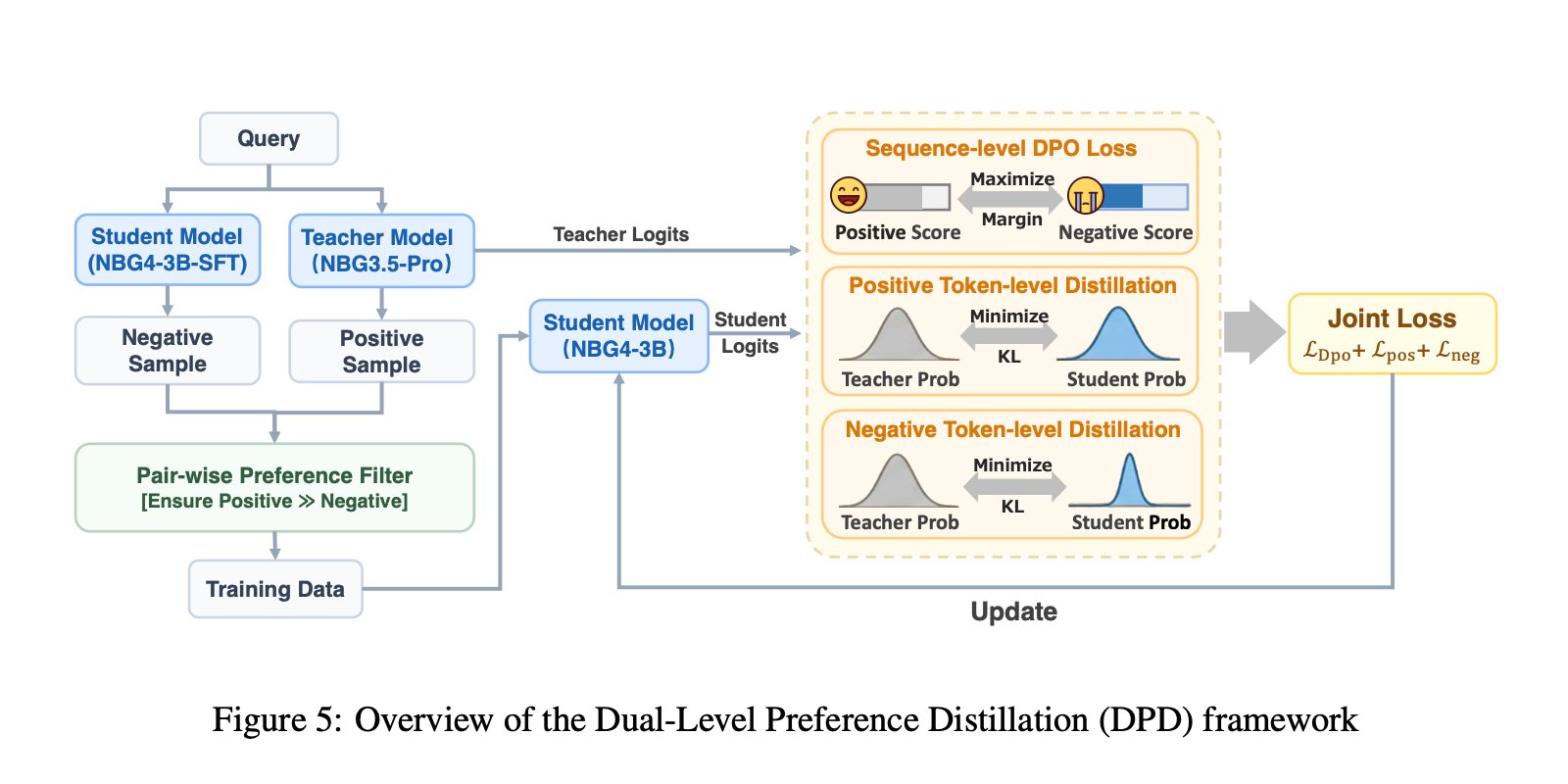
DPD distillation, then multi-stage RL with verification tools
Distillation uses the preferred two-level distillation, DPD. The student learns symbol-level distributions from the teacher model, while the sequence-level DPO objective maximizes the margin between positive and negative responses. The positives are sampled from the teacher Nanbeige3.5-Pro, the negatives are sampled from the student 3B, and distillation is applied to both types of samples to reduce confident errors and improve alternatives.
Reinforcement learning is organized by domain, and each stage uses a GRPO policy. The research team describes filtering policy data using an average success rate of 16 and keeping samples strictly between 10% and 90% to avoid trivial or impossible artifacts. STEM RL uses a proxy checker that calls the Python interpreter to check parity outside of string matching. Coding RL uses synthetic test functions, validated by sandbox execution, and uses success rewards from those tests. Human preference alignment (RL) uses a binary reward model designed to reproduce preferences in a small number of tokens and reduce the risk of reward compromise compared to common language model rewards.

Comparison table
| Standard, metric | Qwen3-14B-2504 | Qwen3-32B-2504 | Nanbej 4-3B-2511 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AIME2024, average @8 | 79.3 | 81.4 | 90.4 |
| AIME2025, average @8 | 70.4 | 72.9 | 85.6 |
| GPQA-Diamond, average @3 | 64.0 | 68.7 | 82.2 |
| SuperGPQA, average @3 | 46.8 | 54.1 | 53.2 |
| PVCL-V4, Average @ 3 | 45.4 | 47.9 | 53.8 |
| Fullstack seat, average @3 | 55.7 | 58.2 | 48.0 |
| ArenaHard-V2, average @3 | 39.9 | 48.4 | 60.0 |
Key takeaways
- 3B can drive much larger open models in inference, given the average sample setting of the paper. Nanbeige4-3B-Thinking reports AIME 2024 avg@8 90.4 vs Qwen3-32B 81.4, and GPQA-Diamond avg@3 82.2 vs Qwen3-14B 64.0.
- The research team is careful to evaluate, these are average @k results with specific decoding, not single shot resolution. The AIME is avg@8, most others are avg@3, with a temperature of 0.6, a maximum p of 0.95, and a long maximum generation.
- Pretraining gains are related to data approaches, not just more codes. Fine-grained WSD schedules higher quality mixtures later, and 1B ablation shows GSM8K moving from 27.1 to 34.3 versus vanilla scheduling.
- Post-training focuses on the quality of supervision, followed by preference-aware distillation. The pipeline uses trading solution optimization combined with chain-of-thought reconstruction, then dual preference distillation that combines token distribution matching with chain-level preference optimization.
verify Paper weights and forms. Feel free to check out our website GitHub page for tutorials, codes, and notebooks. Also, feel free to follow us on twitter Don’t forget to join us 100k+ mil SubReddit And subscribe to Our newsletter. I am waiting! Are you on telegram? Now you can join us on Telegram too.

Michel Sutter is a data science specialist and holds a Master’s degree in Data Science from the University of Padova. With a solid foundation in statistical analysis, machine learning, and data engineering, Michelle excels at transforming complex data sets into actionable insights.

Don’t miss more hot News like this! Click here to discover the latest in AI news!
2025-12-13 06:00:00




