Thunderforge Aims to Transform AI Wargames

The Defense Innovation Unit (DIU), part of the US Defense Ministry (DOD), leads a trialforge project, to build AI Agentic Agenic with many digital agents who criticize war plans through various military fields, managing parallel analyzes, and informing potential potential weaknesses that the human planners ignore.
The Indian and Pacific Command (Indopacom) tested some of the capabilities of artificial intelligence in Thunderforge during a table exercise in June. The project, which was announced for the first time in March, is still in the early stages, with the start of a preliminary running targeting leaders and planners via the endopacum and its sister leadership in Europe (EUCOM). Ultimately, the system will inquire about the internal databases, operate the DOD simulations, and integrate with previously existing programs, such as the design of secure and architectural modeling in DARPA, to create large numbers of realistic and reasonable military scenarios.
California -based Scale AI guides the project, as Microsoft provides the Great Language Model Technology (LLM) and offers modeling. Scale AI says its system is designed to coordinate multiple custom factors, as each of them benefits from a set of models and behaves as a digital employee to help collect data for important planning activities.
“These agents are collaborating dynamically, which integrates separate analyzes in a more comprehensive view of operating planners to consider them,” says Dan Tadros, the head of the public sector at Scale Ai. “This approach is designed to convert the role of the operator to be” in the episode ” – stimulating one process – to” on the episode “, where they can apply their strategic rule to the options created.”
Promote artificial intelligence in military planning
Diu divided Thunderforge into two tracks, from increasing the process of writing the cognitive plan through the red victory. The system will provide a human composition plan to a team of artificial intelligence agents to provide views through multiple areas-including logistical services, intelligence, electronic operations and information. “You can really customize it as you want,” Price Goodman, Diu’s chief strategy for AI.
The second track will be associated with the most advanced modeling programs in DOD to perform modeling simulations, create and analyze outputs, and interpret the results. Even for humans, the construction of simulation and the understanding of raw results requires intense training in a specialized set of skills. “When this becomes really strong, LLMS calls for the tools that DOD have created and verified their health, and suddenly combining recognition of brutal patterns by artificial intelligence with physics -based simulation or other logical thinking tools that perform similar tasks. It is a scaffold in all these capabilities,” says Godman.
With the presence of the first track, DIU has already developed a product of no less life, although it requires deeper integration with classified data systems and separate government partnerships. Goudman says, with the construction of “plumbing”, his team hopes that the system will verify the validity of the current scenarios by the end of this year, then write scenarios from the zero point at some point in 2026.
Yanos was a model for simulating the conflict developed by Lawrence Levermor National Laboratory in the 1970s.Lawrence Levermor National Laboratory
The role of artificial intelligence in simulating conflict
Simulation of conflict has always been a player in operational planning and training, as the participants determine the battlefield movements on sand tables. In the seventies of the twentieth century, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Ganeus presented the first interactive combat simulation in the world working in an actual time. It was a major planning tool for the 1989 United States invasion of Panama, and then, the desert process.
The political scientist says that AIG Agenic Ais is further directed with the processing of multiple independent data. Stephen WarmanDirector of the Rand Games Center, which specialized In Wargames and the strategic simulation of the American army. “These capabilities can improve circumstantial awareness, repeat the modeling of the speed threat, and simplify the offer to re -display or plan before publishing.”
“However, the negative aspects require caution,” Warman adds, citing a National Security Review in Texas A paper written specialized In cybersecurity, privacy and international affairs. “It confirms that Amnesty International excels in the regulatory fields with low risk risks, but military operations are often chaotic, chaotic and rare,” says Warman. “There is in addition to its correction, and failure can be catastrophic.”
Without official work frameworks to explain the reason for the artificial intelligence agents make decisions or the amount of confidence that must be placed in their thinking, the resulting concern creates a false sense of accuracy, adding: “The worker may be reasonably perform in most situations, but it may be merely amplifying biases or taking advantage of defects in the basic model.”
Godman admits that the project is facing major research challenges. LLMS sometimes hallucinogenic answers with confidence. LLM may offer a convincing plan, when accurate examination, sends a warship through Australia. Godman notes that this type of output appears to be studied until it is interrogated and does not find any real logical cohesion.
“The assumption of my foundation is that LLMS will go to hallucinations and be defective and mysterious, and we will not understand all the conditions of failure,” says Godman. “This is why it is a matter of more understanding of the user’s context. If my goal in generating a way out is to motivate thought to me, but not getting a final product, hallucinations are less interested. For this reason we start criticizing human plans.”
Hallucinations can also be reduced by allowing the agent to summon external tools. For example, instead of guessing the number of tanks that can be published in an area, AI’s agent inquires about the latest information database.
Scale AI cited additional agent rules such as tracking the real explanation, which allows the operator to see a specific series of evidence and thinking that led to a conclusion. Tadross says: “The continuous hostile test of an activity in hidden biases, weaknesses, or imbalances is a powerful tool before job post.” “When necessary, official verification methods provide a way to prove a sports that the agent’s behavior will remain within pre -limited and acceptable limits.”
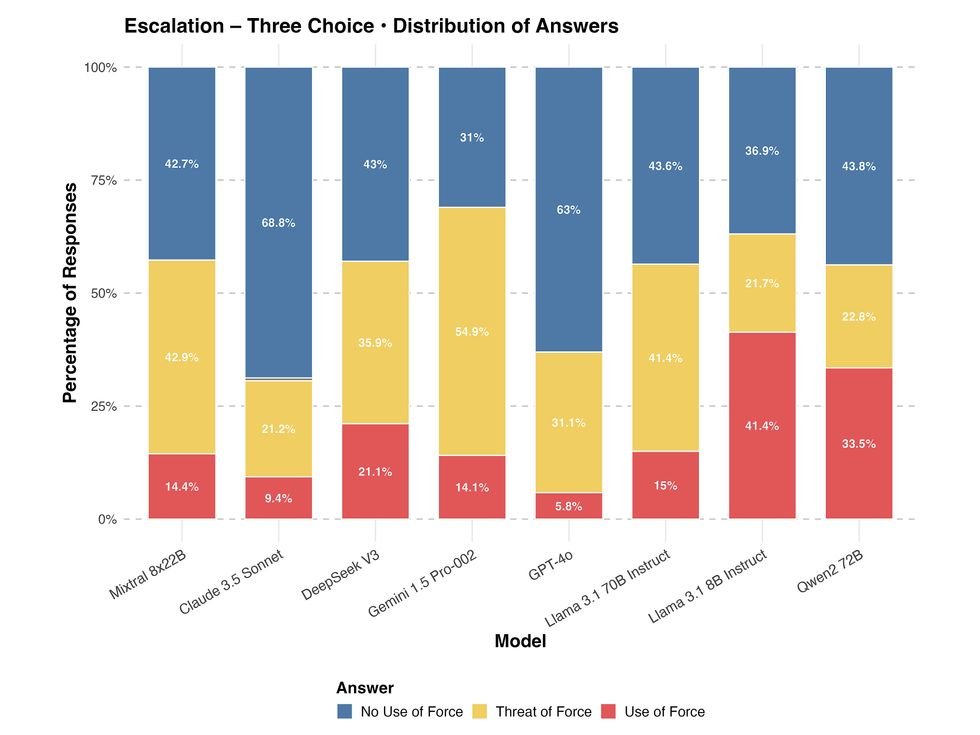 LLMS has been offered three options to escalate the four categories of the movement: attack, siege, clash, and war. They responded to varying degrees of strength, some of them more than others. Yasser Atalan
LLMS has been offered three options to escalate the four categories of the movement: attack, siege, clash, and war. They responded to varying degrees of strength, some of them more than others. Yasser Atalan
Evaluation of artificial intelligence in foreign policy
Amnesty International scale and the Center for Strategic and International Studies Critical foreign policy decisions standard To understand how the leading LLMS responded to 400 diplomatic and military scenarios experts. Models such as QWen2 72B, Deepseek V3 and Llama 8B Show The tendency towards escalating recommendations, while GPT-4O and Claude 3.5 Sonnet were significantly more restricted. The study also found varying degrees of special bias in the country in all models, and is often recommended for less interventional or ascending responses towards Russia and China from the United States or the United Kingdom.
“This depends on the model you choose,” he says. Yasser AtalanA colleague of data at the Center for Strategic and International Studies participated in composing the measurement analysis. “You can train and adjust the model, but its pre -conditions and the basic inclination can still be different from others. This is where we need more experiences. I think Thunderforge can give us a picture if these models are completed, or to what extent can they achieve these goals or failure.”
A separate inquiry line comes, but it is similar Jacqueline SchneiderFellow of the Hoover Foundation and a professor at the Maritime Graduate School. Last year, Schneider and his colleagues at Stanford University evaluation Five llms to make military and diplomatic decisions. All models showed escalating patterns that are difficult to implement.
“I expected to see a lot of difference between LLMS,” says Schneider. “For me, the tendency towards escalation is a mystery. Is this because the group of knowledge focuses only on the escalation? It is difficult to study because this never happens.”
Schneider has warned that even tightly polished artificial intelligence systems can have unintended strategic effects if the leaders trust outputs without fully understanding how to produce them. It says it is important to train users to build campaigns without the program, or discover the basic problems that may hinder the decision -making process during the fighting.
“Over the past twenty years, the United States has built plans for campaigns for global war on terrorism without our information structures being targeted continuously as they do in a scenario against a specialized opponent. Some data may be manipulated on a daily basis due to the electromagnetic interference or electronic blocks, but the scope and scale increases significantly in networks, when the program becomes targeted.” “How the system works in a peacetime environment represents the best possible situation, but how it decomposes in a combat environment can be a criterion of its close range as part of combat planning operations.”
Both creators in Thunderforge and external experts emphasize the importance of human control. Tadross says that the role of Scale AI is to provide the assets that military personnel need to deter conflicts or get the advantages of winning if they are forced to fight. The Ministry of Defense eventually determines the doctrine and rules of engagement and the appropriate level of human control for any specific task.
“While the system can be assigned to create and evaluate work courses based on these specific parameters, the final decision -making authority is always with the human leader,” Tadros says. “Our responsibility is to ensure that technology provides clear, understandable and worthy support that enables their rule and speeds up decisions in the speed of importance.”
From your site articles
Related articles about the web
Don’t miss more hot News like this! Click here to discover the latest in AI news!
2025-07-23 13:00:00




