Solar-Powered Device Turns Moon Dirt Into Bricks, a Potential Breakthrough in Lunar Construction

Both the United States and China put their eyes on the moon, with the aim of opening the Earth to the permanent rules of the moon during the next decade. Although there is no legal basis for land claiming in space, any country that gets there will first get the first desired feature of the engine, allowing it to set certain basic bases around who can do, where.
But reaching there is only half of the battle. In fact, the creation of a continuous satellite represents logistical challenges and great engineering. One of the largest obstacles is to know how to transfer building materials efficiently and affordable prices to create a base of the moon, but a team of scientists at the DSEL space exploration laboratory in Hefei, Anhui province, may have already solved this problem.
In July, the researchers published the test results of a preliminary model of the moon formation system in Acta Asta Routleutica. This 3D printer device makes a strong building brick from Moondust, also known as the Rego Lunar. Yang Hoglon, a co -author and a great engineer in DSEL, told Chinese government media agency Xinhua to be able to produce building materials with resources available on the surface of the moon that would reduce the need for Earth’s materials.
“This penetration of printing led to the feasibility of the use of lunar soil as a single raw building material, allowing the use of real resources on the site and getting rid of the need to transfer any additional materials from the ground,” said Yang.
The system uses a reward mirror – a reflector dish – to collect solar radiation, focus it at one point, then it is converted through packages of optical cables fiber. At the focus point, the intensity of light exceeds 3000 times of the standard density of sunlight on the surface of the Earth, reaching temperatures more than 2300 ° F (1300 ° C), according to the Moon Moon daily. This is generally hot enough to dissolve Moondust.
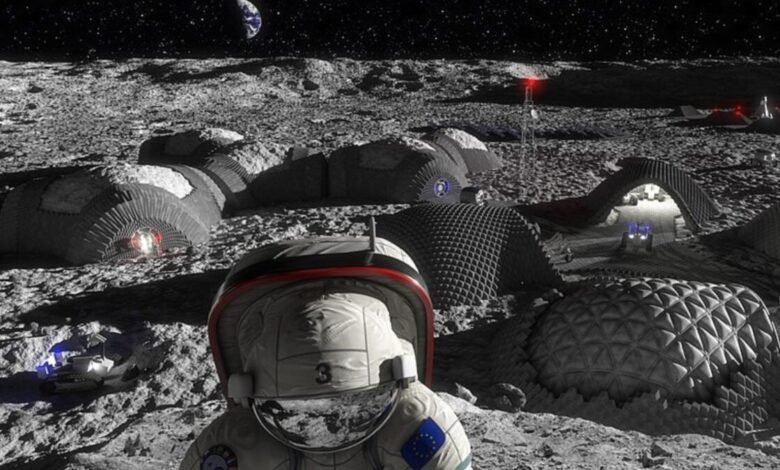
In a series of laboratory tests using the satellite reigoliths made of basalt and Xenon lamp to simulate sunlight, the initial model succeeded in melting the solid shapes that were formed, including lines, surfaces, bodies and complex structures. Yang claims that the initial model can manufacture materials to support the building of lunar roads, equipment and buildings to enable lunar exploration on a large scale, sustainable and use of resources.
The success of this initial test is a big step towards the manufacture of lunar building materials on the site, but there are restrictions. Yang Moon Daily told the lunar soil bricks that could not maintain pressure in the moon’s environment and a low gravitational environment. However, they can act as preventive layers on habitat units that maintain pressure made of solid and inflatable structures, according to the daily Moon reports.
China had already chosen major steps in this field before DSEL researchers tested their moon formation system. In November 2024, the nation sent a shipping missile bearing preliminary brick models made of simulator simulator to the Tiangong space station for testing in space conditions. Bricks will remain outside the space station for a period of three years to test their durability in this harsh environment, according to the Space.com website.
Other countries, including the United States, are also developing ways to use the lunar Reagate to build, but China has advanced over the past few years has been especially important. In fact, the Chinese Moon Exploration Program with the ARTEMIS of the ARTEMIS program of the ARTEMIS of NASA – has even exceeded – over the past few years. The United States definitely feels pressure.
Don’t miss more hot News like this! Click here to discover the latest in Technology news!
2025-08-08 10:00:00