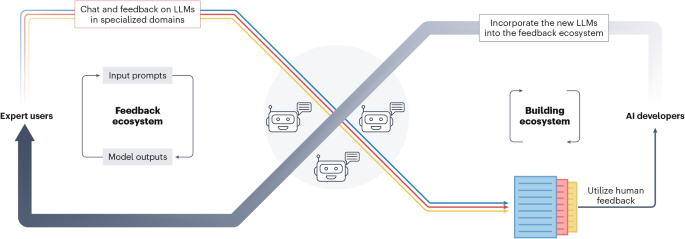
The future of open human feedback
Radford, A. et al. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 1, 9 (2019).
Ivanova, A. A. et al. Elements of World Knowledge (EWOK): a cognition-inspired framework for evaluating basic world knowledge in language models. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2405.09605 (2024).
Schick, T. et al. Toolformer: language models can teach themselves to use tools. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 36, 332 (2024).
Imran, M. & Almusharraf, N. Analyzing the role of chatGPT as a writing assistant at higher education level: a systematic review of the literature. Contemp. Educ. Technol. 15, ep464 (2023).
Google Scholar
Barke, S., James, M. B. & Polikarpova, N. Grounded copilot: how programmers interact with code-generating models. Proc. ACM Program. Lang. 7, 85–111 (2023).
Google Scholar
Askell, A. et al. A General language assistant as a laboratory for alignment. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2112.00861 (2021).
Ouyang, L. et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 27730–27744 (2022).
Dang, J et al. RLHF can speak many languages: unlocking multilingual preference optimization for LLMs. In Proc. 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing 13134–13156 (ACL, 2024).
Bai, Y. et al. Training a helpful and harmless assistant with reinforcement learning from human feedback. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2204.05862 (2022).
Thoppilan, R. et al. LaMDA: language models for dialog applications. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2201.08239 (2022).
Nakano, R. et al. WebGPT: browser-assisted question-answering with human feedback. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2112.09332 (2021).
Wang, Z. et al. HelpSteer2: open-source dataset for training top-performing reward models. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2406.08673 (2024).
Ahmadian, A. et al. Back to basics: revisiting REINFORCE-style optimization for learning from human feedback in LLMs. In Proc. 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics Vol. 1 (ACL, 2024).
Patel, D. & Ahmad, A. Google “we have no moat, and neither does openAI”. SemiAnalysis https://semianalysis.com/2023/05/04/google-we-have-no-moat-and-neither/ (4 May 2023).
Introducing Meta Llama 3: the most capable openly available LLM to date. MetaAI https://ai.meta.com/blog/meta-llama-3/ (2024).
Boubdir, M., Kim, E., Ermis, B., Fadaee, M. & Hooker, S. Which prompts make the difference? Data prioritization for efficient human LLM evaluation. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2310.14424 (2023).
Singh, S. et al. Aya dataset: an open-access collection for multilingual instruction tuning. In Proc. 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics Vol. 1 (ACL, 2024).
Li, N. et al. The WMDP benchmark: measuring and reducing malicious use with unlearning. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2403.03218 (2024).
AI @ Meta Llama Team. The Llama 3 herd of models. (2024).
Stiennon, N. et al. Learning to summarize with human feedback. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 3008–3021 (2020).
Lambert, N., Tunstall, L., Rajani, N. & Thrush, T. HuggingFace H4 stack exchange preference dataset. Hugging Face https://huggingface.co/datasets/HuggingFaceH4/stack-exchange-preferences (2023).
Cui, G. et al. ULTRAFEEDBACK: boosting language models with scaled AI feedback. In International Conference on Machine Learning (PMLR, 2024).
Taori, R. et al. Stanford Alpaca: an instruction-following Llama model. GitHub https://github.com/tatsu-lab/stanford_alpaca (2023).
Aakanksha, A. A. et al. The multilingual alignment prism: aligning global and local preferences to reduce harm. In Proc. 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing 12027–12049 (ACL, 2024).
Zhao, W. et al. Wildchat: 1m ChatGPT interaction logs in the wild. In 12th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2024).
Zheng, L. et al. Judging LLM-as-a-judge with MT-Bench and Chatbot Arena. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 36, 46595–46623 (2023).
Kirk, H. R. et al. The PRISM alignment dataset: What participatory, representative and individualised human feedback reveals about the subjective and multicultural alignment of large language models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process Syst. 37, 105236–105344 (2024).
Aroyo, L. et al. DICES dataset: diversity in conversational AI evaluation for safety. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2306.11247 (2023).
Don-Yehiya, S., Choshen, L. & Abend, O. The ShareLM collection and plugin: contributing human-model chats for the benefit of the community. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2408.08291 (2024).
Köpf, A. et al. OpenAssistant Conversations—democratizing large language model alignment. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2304.07327 (2024).
Agnew, W. et al. The illusion of artificial inclusion. In Proc. CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems 1–12 (ACM, 2024).
White, M. et al. The model openness framework: promoting completeness and openness for reproducibility, transparency and usability in AI. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2403.13784 (2024).
Liesenfeld, A. & Dingemanse, M. Rethinking open source generative AI: open washing and the EU AI Act. In The 2024 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency 1774–1787 (2024).
Zheng, L. et al. LMSYS-Chat-1M: a large-scale real-world LLM conversation dataset. In The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations (2024).
Benkler, Y. The Wealth of Networks: How Social Production Transforms Markets and Freedom (Yale Univ. Press, 2007).
Halfaker, A. & Geiger, R. S. ORES: lowering barriers with participatory machine learning in Wikipedia. In Proc. ACM Human–Computer Interaction Vol. 4 https://doi.org/10.1145/3415219 (2020).
Palen, L., Soden, R., Anderson, T. J. & Barrenechea, M. Success & scale in a data-producing organization: the socio-technical evolution of OpenStreetMap in response to humanitarian events. In Proc. 33rd Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems 4113–4122 (ACM, 2015).
Bryant, S. L., Forte, A. & Bruckman, A. Becoming Wikipedian: transformation of participation in a collaborative online encyclopedia. In Proc. 2005 ACM International Conference on Supporting Group Work 1–10 (ACM, 2005).
Balestra, M., Cheshire, C., Arazy, O. & Nov, O. Investigating the motivational paths of peer production newcomers. In Proc. 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems 6381–6385 (ACM, 2017).
Kriplean, T., Beschastnikh, I. & McDonald, D. W. Articulations of wikiwork: uncovering valued work in Wikipedia through barnstars. In Proc. 2008 ACM Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work 47–56 (ACM, 2008).
Mamykina, L., Manoim, B., Mittal, M., Hripcsak, G. & Hartmann, B. Design lessons from the fastest Q&A site in the west. In Proc. SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 2857–2866 (ACM, 2011).
Movshovitz-Attias, D., Movshovitz-Attias, Y., Steenkiste, P. & Faloutsos, C. Analysis of the reputation system and user contributions on a question answering website: Stack Overflow. In Proc. 2013 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining 886–893 (ACM, 2013).
Deci, E. L. Effects of externally mediated rewards on intrinsic motivation. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 18, 105 (1971).
Google Scholar
Ryan, R. M. & Deci, E. L. Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation from a self-determination theory perspective: definitions, theory, practices, and future directions. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 61, 101860 (2020).
Google Scholar
Heltweg, P. & Riehle, D. A systematic analysis of problems in open collaborative data engineering. Trans. Soc. Comput. https://doi.org/10.1145/3629040 (2023).
Fang, J., Liang, J.-W. & Wang, H.-C. How people initiate and respond to discussions around online community norms: a preliminary analysis on meta stack overflow discussions. In Companion Publication of the 2023 Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing 221–225 (ACM, 2023).
Butler, B., Joyce, E. & Pike, J. Don’t look now, but we’ve created a bureaucracy: the nature and roles of policies and rules in Wikipedia. In Proc. SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems 1101–1110 (ACM, 2008).
Zuckerman, E. & Rajendra-Nicolucci, C. From community governance to customer service and back again: re-examining pre-web models of online governance to address platforms’ crisis of legitimacy. Soc. Media Soc. 9, 20563051231196864 (2023).
Google Scholar
Hwang, S. & Shaw, A. Rules and rule-making in the five largest wikipedias. In Proc. International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media Vol. 16, 347–357 (2022).
Kuo, T.-S. et al. Wikibench: community-driven data curation for ai evaluation on wikipedia. In Proc. CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (ACM, 2024).
Masakhane, M. et al. Masakhane—machine translation for Africa. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2003.11529 (2020).
Peng, B. et al. RWKV: reinventing RNNs for the transformer era. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 14048–14077 (ACL, 2023).
Scao, T. L. et al. BLOOM: a 176b-parameter open-access multilingual language model. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2211.05100 (2022).
Biderman, S. et al. Pythia: a suite for analyzing large language models across training and scaling. In International Conference on Machine Learning 2397–2430 (PMLR, 2023).
Ding, J., Akiki, C., Jernite, Y., Steele, A. L. & Popo, T. Towards openness beyond open access: user journeys through 3 open AI collaboratives. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2301.08488 (2023).
Pistilli, G., Muñoz Ferrandis, C., Jernite, Y. & Mitchell, M. Stronger together: on the articulation of ethical charters, legal tools, and technical documentation in ML. In Proc. 2023 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency 343–354 (ACM, 2023).
Hughes, S. et al. The BigCode project governance card. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2312.03872 (2023).
The open source definition. (v1.9) OSI https://opensource.org/osd/ (2007).
Brown, E. M. et al. Measuring software innovation with open source software development data. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2411.05087 (2024).
Langenkamp, M. & Yue, D. N. How open source machine learning software shapes AI. In Proc. 2022 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society 385–395 (2022).
Osborne, C., Ding, J. & Kirk, H. R. The AI community building the future? A quantitative analysis of development activity on Hugging Face hub. J. Comput. Soc. Sci. 7, 1–39 (2024).
Kherroubi Garcia, I. et al. Ten simple rules for good model-sharing practices. PLoS Computat. Biol. 21, e1012702 (2025).
Google Scholar
Bonaccorsi, A. & Rossi, C. Comparing motivations of individual programmers and firms to take part in the open source movement: from community to business. Knowl. Technol. Policy 18, 40–64 (2006).
Google Scholar
Osborne, C. Why companies “democratise” artificial intelligence: the case of open source software donations. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2409.17876 (2024).
Lakhani, K. R. & Wolf, R. G. Why hackers do what they do: understanding motivation and effort in free/open source software projects. Preprint at SSRN https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.443040 (2005).
Shah, S. K. Motivation, governance, and the viability of hybrid forms in open source software development. Manag. Sci. 52, 1000–1014 (2006).
Google Scholar
Subramanyam, R. & Xia, M. Free/libre open source software development in developing and developed countries: a conceptual framework with an exploratory study. Decis. Support Syst. 46, 173–186 (2008).
Google Scholar
Takhteyev, Y. Coding Places: Software Practice in a South American City (MIT Press, 2012).
Von Krogh, G., Haefliger, S., Spaeth, S. & Wallin, M. W. Carrots and rainbows: motivation and social practice in open source software development. MIS Q. 649–676 (2012).
Li, X. et al. Systematic literature review of commercial participation in open source software. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 34, 33 (2024).
Lindman, J., Juutilainen, J.-P. & Rossi, M. Beyond the business model: incentives for organizations to publish software source code. In IFIP International Conference on Open Source Systems (eds Boldyreff, C. et al.) 47–56 (Springer, 2009).
Birkinbine, B. Incorporating the Digital Commons: Corporate Involvement in Free and Open Source Software (Univ. Westminster Press, 2020).
Fink, M. The Business and Economics of Linux and Open Source (Prentice Hall Professional, 2003).
Lerner, J. & Tirole, J. Some simple economics of open source. J. Ind. Econ. 50, 197–234 (2002).
Google Scholar
Woods, D. & Guliani, G. Open Source for the Enterprise: Managing Risks, Reaping Rewards (‘O’Reilly Media, 2005).
Osborne, C. et al. Characterising open source co-opetition in company-hosted open source software projects: the cases of PyTorch, TensorFlow, and transformers. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2410.18241 (2024).
Pitt, L. F., Watson, R. T., Berthon, P., Wynn, D. & Zinkhan, G. The penguin’s window: corporate brands from an open-source perspective. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 34, 115–127 (2006).
Google Scholar
Osborne, C. Public–private funding models in open source software development: a case study on scikit-learn. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2404.06484 (2024).
Ågerfalk, P. J. & Fitzgerald, B. Outsourcing to an unknown workforce: exploring opensurcing as a global sourcing strategy. MIS Q. 385–409 (2008).
West, J. & Gallagher, S. Challenges of open innovation: the paradox of firm investment in open-source software. R&D Manag. 36, 319–331 (2006).
Google Scholar
O’Mahony, S. & Bechky, B. A. Boundary organizations: enabling collaboration among unexpected allies. Admin. Sci. Q. 53, 422–459 (2008).
Google Scholar
Germonprez, M., Allen, J. P., Warner, B., Hill, J. & McClements, G. Open source communities of competitors. ACM Interact. 20, 54–59 (2013).
Google Scholar
Goggins, S., Lumbard, K. & Germonprez, M. Open source community health: analytical metrics and their corresponding narratives. In 2021 IEEE/ACM 4th International Workshop on Software Health in Projects, Ecosystems and Communities 25–33 (IEEE, 2021).
Pipatanakul, K. et al. Typhoon: Thai large language models. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2312.13951 (2023).
Birhane, A. et al. Power to the people? Opportunities and challenges for participatory AI. In Proc. 2nd ACM Conference on Equity and Access in Algorithms, Mechanisms, and Optimization 1–8 (ACM, 2022).
Sloane, M., Moss, E., Awomolo, O. & Forlano, L. Participation is not a design fix for machine learning. In Proc. 2nd ACM Conference on Equity and Access in Algorithms, Mechanisms, and Optimization 1–6 (ACM, 2022).
Krishnamurthy, S. & Tripathi, A. K. Bounty programs in free/libre/open source software. In The Economics of Open Source Software Development https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:107939629 (2006).
Chen, S., Epps, J., Ruiz, N. & Chen, F. Eye activity as a measure of human mental effort in HCI. In Proc. 16th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces 315–318 (ACM, 2011).
Ash, J., Anderson, B., Gordon, R. & Langley, P. Digital interface design and power: friction, threshold, transition. Environ. Plann. D 36, 1136–1153 (2018).
Google Scholar
Lin, B. Y. et al. WildBench: benchmarking LLMs with challenging tasks from real users in the wild. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2406.04770 (2024).
Hancock, B., Bordes, A., Mazare, P.-E. & Weston, J. Learning from dialogue after deployment: feed yourself, chatbot! In Proc. 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (eds Korhonen, A. et al.) 3667–3684 (ACL, 2019).
Don-Yehiya, S., Choshen, L. & Abend, O. Naturally occurring feedback is common, extractable and useful. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2407.10944 (2024).
Gougherty, A. V. & Clipp, H. L. Testing the reliability of an AI-based large language model to extract ecological information from the scientific literature. npj Biodiversity 3, 13 (2024).
Google Scholar
Pokrywka, J., Kaczmarek, J. & Gorzela’nczyk, E. GPT-4 passes most of the 297 written Polish board certification examinations. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:269588160 (2024).
Merlyn mind’s education-domain language models. Merlyn Mind AI Team https://www.merlyn.org/blog/merlyn-minds-education-specific-language-models (2023).
Rein, D. et al. GPQA: a graduate-level google-proof Q&A benchmark. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2311.12022 (2023).
Wu, S. et al. BloombergGPT: a large language model for finance. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2303.17564 (2023).
Liu, X.-Y., Wang, G. & Zha, D. FinGPT: democratizing internet-scale data for financial large language models. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2307.10485 (2023).
Klie, J.-C. et al. Lessons learned from a citizen science project for natural language processing. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2304.12836 (2023).
Pavlick, E., Post, M., Irvine, A., Kachaev, D. & Callison-Burch, C. The language demographics of Amazon Mechanical Turk. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2, 79–92 (2014).
Google Scholar
Zhao, W. et al. UNcommonsense reasoning: abductive reasoning about uncommon situations. In Proc. 2024 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies Vol. 1 (eds Duh, K. et al.) 8487–8505 (ACL, 2024).
Seth, A., Ahuja, S., Bali, K. & Sitaram, S. DOSA: a dataset of social artifacts from different Indian geographical subcultures. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2403.14651 (2024).
Emerson, R. W. Convenience sampling, random sampling, and snowball sampling: how does sampling affect the validity of research? J. Vis. Impair. Blind. 109, 164–168 (2015).
Google Scholar
Watts, I. et al. Pariksha: a scalable, democratic, transparent evaluation platform for assessing indic large language models. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2406.15053 (2024).
Quaye, J. et al. Adversarial nibbler: an open red-teaming method for identifying diverse harms in text-to-image generation. In The 2024 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency 388–406 (ACM, 2024).
Tsatsou, P. Digital divides revisited: what is new about divides and their research? Media Cult. Soc 33, 317–331 (2011).
Google Scholar
Avle, S., Quartey, E. & Hutchful, D. Research on mobile phone data in the global south: opportunities and challenges. Preprint at UMass Amherst https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780190460518.013.33 (2018).
Lu, Y., Zhu, W., Li, L., Qiao, Y. & Yuan, F. LLaMAX: scaling linguistic horizons of llm by enhancing translation capabilities beyond 100 languages. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2407.05975 (2024).
Peters, D. et al. Participation is not enough: towards indigenous-led co-design. In Proc. 30th Australian Conference on Computer-Human Interaction 97–101 (ACM, 2018).
Santurkar, S. et al. Whose opinions do language models reflect? In International Conference on Machine Learning 29971–30004 (PMLR, 2023).
Pozzobon, L., Ermis, B., Lewis, P. & Hooker, S. Goodtriever: adaptive toxicity mitigation with retrieval-augmented models. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2310.07589 (2023).
Kiela, D. et al. Dynabench: rethinking benchmarking in NLP. In Proc. 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (eds Toutanova, K. et al.) 4110–4124 (ACL, 2021).
White, C. et al. LiveBench: a challenging, contamination-free LLM benchmark. In 13th International Conference on Learning Representations. (ICLR, 2015).
BigCode. Am I in The Stack? Hugging Face https://huggingface.co/spaces/bigcode/in-the-stack (2024).
European parliament and Council of the European Union. Regulation (EU) 2016/679 of the European Parliament and of the Council https://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2016/679/oj (2016).
Illman, E. & Temple, P. California consumer privacy act. Bus. Lawyer 75, 1637–1646 (2019).
Accountability Act. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996. Public law 104, 191 (1996).
Kumar, M., Moser, B., Fischer, L. & Freudenthaler, B. Towards practical secure privacy-preserving machine (deep) learning with distributed data. In International Conference on Database and Expert Systems Applications 55–66 (Springer, 2022).
Raji, I. D. et al. Closing the AI accountability gap: defining an end-to-end framework for internal algorithmic auditing. In Proc. 2020 Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency 33–44 (ACM, 2020).
Bender, E. M., Gebru, T., McMillan-Major, A. & Shmitchell, S. On the dangers of stochastic parrots: can language models be too big? In Proc. 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency 610–623 (ACM, 2021).
The NIST Privacy Framework: A Tool for Improving Privacy through Enterprise Risk Management (NIST, 2020); https://www.nist.gov/privacy-framework/privacy-framework
Narayanan, A. & Shmatikov, V. Robust de-anonymization of large sparse datasets. In 2008 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy 111–125 (IEEE, 2008).
Dwork, C., McSherry, F., Nissim, K. & Smith, A. Calibrating noise to sensitivity in private data analysis. In Proc. Theory of Cryptography: Third Theory of Cryptography Conference 265–284 (Springer, 2006).
Dwork, C. et al. The algorithmic foundations of differential privacy. Found. Trends Theor. Comput. Sci. 9, 211–407 (2014).
Google Scholar
Cummings, R. et al. Challenges towards the next frontier in privacy. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2304.06929 (2023).
Liu, Z., Iqbal, U. & Saxena, N. Opted out, yet tracked: are regulations enough to protect your privacy? Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2304.06929 (2022).
Tran, V. H. et al. Measuring compliance with the california consumer privacy act over space and time. In Proc. CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems 1–19 (2024).
Bourtoule, L. et al. Machine unlearning. In 2021 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy 141–159 (IEEE 2021).
Lynch, A., Guo, P., Ewart, A., Casper, S. & Hadfield-Menell, D. Eight methods to evaluate robust unlearning in LLMs. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2402.16835 (2024).
Shi, W. et al. MUSE: machine unlearning six-way evaluation for language models. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2407.06460 (2024).
Guadamuz, A. Artificial intelligence and copyright. Wipo Mag. 5, 14–19 (2017).
Terms of use. OpenAI https://openai.com/policies/terms-of-use/ (2024).
Kop, M. AI & intellectual property: towards an articulated public domain. Univ. Texas School Law Texas Intellect. Prop. Law J. 28, (2020).
Kim, M. The creative commons and copyright protection in the digital era: uses of creative commons licenses. J. Comput. Mediat. Commun. 13, 187–209 (2007).
Google Scholar
Bonatti, P., Kirrane, S., Polleres, A. & Wenning, R. Transparent personal data processing: the road ahead. In Proc. Computer Safety, Reliability, and Security: SAFECOMP 2017 Workshops, ASSURE, DECSoS, SASSUR, TELERISE, and TIPS 337–349 (Springer, 2017).
Gebru, T. et al. Datasheets for datasets. Commun. ACM 64, 86–92 (2021).
Google Scholar
Shimorina, A. & Belz, A. The Human Evaluation Datasheet 1.0: a template for recording details of human evaluation experiments in NLP. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2103.09710 (2021).
Pushkarna, M., Zaldivar, A. & Kjartansson, O. Data cards: purposeful and transparent dataset documentation for responsible AI. In Proc. 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency 1776–1826 (2022).
Iren, D. & Bilgen, S. Cost of quality in crowdsourcing. Hum. Comput. https://doi.org/10.15346/hc.v1i2.14 (2014).
Hettiachchi, D. et al. Investigating and mitigating biases in crowdsourced data. In Companion Publication of the 2021 Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing 331–334 (ACM, 2021).
Barbosa, N. M. & Chen, M. Rehumanized crowdsourcing: a labeling framework addressing bias and ethics in machine learning. In Proc. 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems 1–12 (ACM, 2019).
Chintala, S. Unapologetically open science—the complexity and challenges of making openness win! ICML https://icml.cc/virtual/2024/invited-talk/35249 (2024).
Chiang, Wei-Lin, et al. Chatbot arena: An open platform for evaluating llms by human preference. In 41st International Conference on Machine Learning (PMLR, 2024).
Nov, O., Arazy, O. & Anderson, D. Scientists@ home: what drives the quantity and quality of online citizen science participation? PLoS ONE 9, e90375 (2014).
Google Scholar
Chen, Y., Harper, F. M., Konstan, J. & Li, S. X. Social comparisons and contributions to online communities: a field experiment on movielens. Am. Econ. Rev. 100, 1358–1398 (2010).
Google Scholar
Pustejovsky, J. & Stubbs, A. Natural Language Annotation for Machine Learning: A Guide to Corpus-building for Applications (O’Reilly Media, 2012).
Thorat, P. B., Goudar, R. M. & Barve, S. Survey on collaborative filtering, content-based filtering and hybrid recommendation system. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 110, 31–36 (2015).
Touvron, H. et al. Llama 2: open foundation and fine-tuned chat models. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2307.09288 (2023).
Achiam, J. et al. GPT-4 technical report. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2303.08774 (2023).
Model card and evaluations for Claude models. Anthropic https://www.anthropic.com/news/claude-2 (2023).
The Claude 3 model family: Opus, Sonnet, Haiku. Anthropic https://www.anthropic.com/claude-3-model-card (2024).
Gemini Team et al. Gemini: a family of highly capable multimodal models. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2312.11805 (2023).
Reid, M. et al. Gemini 1.5: unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2403.05530 (2024).
Don’t miss more hot News like this! Click here to discover the latest in AI news!
2025-06-20 00:00:00




